Analyzing Large Language Models' Responses to Common Lumbar Spine Fusion Surgery Questions: A Comparison Between ChatGPT and Bard
- PMID: 38955533
- PMCID: PMC11224745
- DOI: 10.14245/ns.2448098.049
Analyzing Large Language Models' Responses to Common Lumbar Spine Fusion Surgery Questions: A Comparison Between ChatGPT and Bard
Abstract
Objective: In the digital age, patients turn to online sources for lumbar spine fusion information, necessitating a careful study of large language models (LLMs) like chat generative pre-trained transformer (ChatGPT) for patient education.
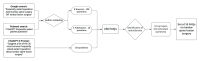
Methods: Our study aims to assess the response quality of Open AI (artificial intelligence)'s ChatGPT 3.5 and Google's Bard to patient questions on lumbar spine fusion surgery. We identified 10 critical questions from 158 frequently asked ones via Google search, which were then presented to both chatbots. Five blinded spine surgeons rated the responses on a 4-point scale from 'unsatisfactory' to 'excellent.' The clarity and professionalism of the answers were also evaluated using a 5-point Likert scale.
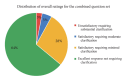
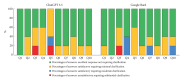
Results: In our evaluation of 10 questions across ChatGPT 3.5 and Bard, 97% of responses were rated as excellent or satisfactory. Specifically, ChatGPT had 62% excellent and 32% minimally clarifying responses, with only 6% needing moderate or substantial clarification. Bard's responses were 66% excellent and 24% minimally clarifying, with 10% requiring more clarification. No significant difference was found in the overall rating distribution between the 2 models. Both struggled with 3 specific questions regarding surgical risks, success rates, and selection of surgical approaches (Q3, Q4, and Q5). Interrater reliability was low for both models (ChatGPT: k = 0.041, p = 0.622; Bard: k = -0.040, p = 0.601). While both scored well on understanding and empathy, Bard received marginally lower ratings in empathy and professionalism.
Conclusion: ChatGPT3.5 and Bard effectively answered lumbar spine fusion FAQs, but further training and research are needed to solidify LLMs' role in medical education and healthcare communication.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Bard; ChatGPT; Large language models; Lumbar spine fusion; Patient education.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Gaudin D, Krafcik BM, Mansour TR, et al. Considerations in spinal fusion surgery for chronic lumbar pain: psychosocial factors, rating scales, and perioperative patient education-a review of the literature. World Neurosurg. 2017;98:21–7. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Z, Yang H, He J, et al. The Impact of treatment-related internet health information seeking on patient compliance. Telemed J E Health. 2021;27:513–24. - PubMed
-
- Cline RJ, Haynes KM. Consumer health information seeking on the Internet: the state of the art. Health Educ Res. 2001;16:671–92. - PubMed
-
- Langford AT, Roberts T, Gupta J, et al. Impact of the internet on patient-physician communication. Eur Urol Focus. 2020;6:440–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

