Epithelial cells maintain memory of prior infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae through di-methylation of histone H3
- PMID: 38956024
- PMCID: PMC11219877
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49347-1
Epithelial cells maintain memory of prior infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae through di-methylation of histone H3
Abstract
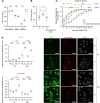
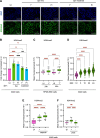
Epithelial cells are the first point of contact for bacteria entering the respiratory tract. Streptococcus pneumoniae is an obligate human pathobiont of the nasal mucosa, carried asymptomatically but also the cause of severe pneumoniae. The role of the epithelium in maintaining homeostatic interactions or mounting an inflammatory response to invasive S. pneumoniae is currently poorly understood. However, studies have shown that chromatin modifications, at the histone level, induced by bacterial pathogens interfere with the host transcriptional program and promote infection. Here, we uncover a histone modification induced by S. pneumoniae infection maintained for at least 9 days upon clearance of bacteria with antibiotics. Di-methylation of histone H3 on lysine 4 (H3K4me2) is induced in an active manner by bacterial attachment to host cells. We show that infection establishes a unique epigenetic program affecting the transcriptional response of epithelial cells, rendering them more permissive upon secondary infection. Our results establish H3K4me2 as a unique modification induced by infection, distinct from H3K4me3 or me1, which localizes to enhancer regions genome-wide. Therefore, this study reveals evidence that bacterial infection leaves a memory in epithelial cells after bacterial clearance, in an epigenomic mark, thereby altering cellular responses to subsequent infections and promoting infection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ANR 17 CE12 0007 01 EPIBACTIN/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- 20-PAMR-0011 TheraEPI/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- LBX-62 IBEID AAP/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- FRM608 EQU202003010152/Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (Foundation for Medical Research in France)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

