Development and validation of an intraoperative hypothermia nomograph model for patients undergoing video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy: a retrospective study
- PMID: 38956148
- PMCID: PMC11219828
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66222-7
Development and validation of an intraoperative hypothermia nomograph model for patients undergoing video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy: a retrospective study
Abstract
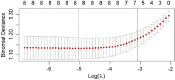
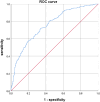
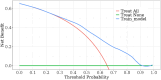
This study aimed to develop and internally validate a nomogram model for assessing the risk of intraoperative hypothermia in patients undergoing video-assisted thoracoscopic (VATS) lobectomy. This study is a retrospective study. A total of 530 patients who undergoing VATS lobectomy from January 2022 to December 2023 in a tertiary hospital in Wuhan were selected. Patients were divided into hypothermia group (n = 346) and non-hypothermia group (n = 184) according to whether hypothermia occurred during the operation. Lasso regression was used to screen the independent variables. Logistic regression was used to analyze the risk factors of hypothermia during operation, and a nomogram model was established. Bootstrap method was used to internally verify the nomogram model. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the discrimination of the model. Calibration curve and Hosmer Lemeshow test were used to evaluate the accuracy of the model. Decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to evaluate the clinical utility of the model. Intraoperative hypothermia occurred in 346 of 530 patients undergoing VATS lobectomy (65.28%). Logistic regression analysis showed that age, serum total bilirubin, inhaled desflurane, anesthesia duration, intraoperative infusion volume, intraoperative blood loss and body mass index were risk factors for intraoperative hypothermia in patients undergoing VATS lobectomy (P < 0.05). The area under ROC curve was 0.757, 95% CI (0.714-0.799). The optimal cutoff value was 0.635, the sensitivity was 0.717, and the specificity was 0.658. These results suggested that the model was well discriminated. Calibration curve has shown that the actual values are generally in agreement with the predicted values. Hosmer-Lemeshow test showed that χ2 = 5.588, P = 0.693, indicating that the model has a good accuracy. The DCA results confirmed that the model had high clinical utility. The nomogram model constructed in this study showed good discrimination, accuracy and clinical utility in predicting patients with intraoperative hypothermia, which can provide reference for medical staff to screen high-risk of intraoperative hypothermia in patients undergoing VATS lobectomy.
Keywords: Intraoperative hypothermia; Nomogram; Prediction model; Risk factors; Video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a prediction model for delayed recovery from anesthesia in elderly lung adenocarcinoma patients underwent thoracoscopic radical resection.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 14;14(1):27983. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79648-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39543272 Free PMC article.
-
Risk assessment of postoperative atelectasis in elderly lung cancer patients undergoing thoracoscopic surgery based on a nomogram model.BMC Surg. 2025 May 12;25(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12893-025-02939-0. BMC Surg. 2025. PMID: 40355856 Free PMC article.
-
[A Nomogram for Prediction of Complications Based on TM&M System of VATS Major Lung Surgery for Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021 Dec 20;24(12):838-846. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2021.103.12. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34923804 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Estimated intraoperative blood loss correlates with postoperative cardiopulmonary complications and length of stay in patients undergoing video-assisted thoracoscopic lung cancer lobectomy: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Surg. 2018 May 23;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12893-018-0360-0. BMC Surg. 2018. PMID: 29792183 Free PMC article.
-
In patients with resectable non-small-cell lung cancer, is video-assisted thoracoscopic segmentectomy an appropriate alternative to video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016 Nov;23(5):826-831. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivw202. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27401084 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning-based prediction model for intraoperative hypothermia risk in thoracoscopic lobectomy patients: A SHAP analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 29;104(35):e44202. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000044202. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40898470 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative thoracic paravertebral block provides greater benefits for body temperature protection in patients undergoing thoracoscopic lung surgery: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Jun 9;25(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03164-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40490717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qing N, Ma HX, Jin GF, et al. Annual progress of the 2022 lung cancer epidemiology study. Chin. Med. J. 2023;103(14):1068–1073. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20221213-02640. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

