Homopolymer switches mediate adaptive mutability in mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancer
- PMID: 38956208
- PMCID: PMC11250277
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01777-9
Homopolymer switches mediate adaptive mutability in mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancer
Abstract
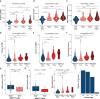
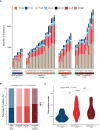
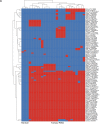
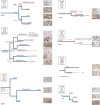
Mismatch repair (MMR)-deficient cancer evolves through the stepwise erosion of coding homopolymers in target genes. Curiously, the MMR genes MutS homolog 6 (MSH6) and MutS homolog 3 (MSH3) also contain coding homopolymers, and these are frequent mutational targets in MMR-deficient cancers. The impact of incremental MMR mutations on MMR-deficient cancer evolution is unknown. Here we show that microsatellite instability modulates DNA repair by toggling hypermutable mononucleotide homopolymer runs in MSH6 and MSH3 through stochastic frameshift switching. Spontaneous mutation and reversion modulate subclonal mutation rate, mutation bias and HLA and neoantigen diversity. Patient-derived organoids corroborate these observations and show that MMR homopolymer sequences drift back into reading frame in the absence of immune selection, suggesting a fitness cost of elevated mutation rates. Combined experimental and simulation studies demonstrate that subclonal immune selection favors incremental MMR mutations. Overall, our data demonstrate that MMR-deficient colorectal cancers fuel intratumor heterogeneity by adapting subclonal mutation rate and diversity to immune selection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures














References
-
- Kunkel TA, Erie DA. DNA mismatch repair. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005;74:681–710. - PubMed
-
- De Wind N, et al. HNPCC-like cancer predisposition in mice through simultaneous loss of Msh3 and Msh6 mismatch-repair protein functions. Nat. Genet. 1999;23:359–362. - PubMed
-
- Sanders, M. A. et al. Life without mismatch repair. Preprint at bioRxiv10.1101/2021.04.14.437578 (2021).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

