Development and validation of the MultiScent-20 digital odour identification test using item response theory
- PMID: 38956288
- PMCID: PMC11219931
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-65915-3
Development and validation of the MultiScent-20 digital odour identification test using item response theory
Abstract
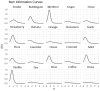
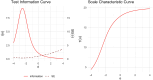
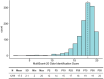
Although validated and reliable psychophysical tests of olfactory function are available, an easy-to-use and feasible test has yet to be developed. This study aimed to design a digital odour identification test, evaluate its validity, assess its reliability, establish a normative curve, and explore the impact of demographic factors. The odour identification test was presented with the Multiscent-20, a hand-held, tablet-like digital scent device that features an integrated odour digital delivery system. The identification performance on the 20 odours was assessed using item response theory (IRT). The normative curve was established by administering the test to a large sample of participants (n = 1299). The mean identification score was 17.5 (SD = 2.1). The two-parameter logistic IRT model provided the best fit, revealing variation in item discrimination and difficulty parameters. Educational attainment influenced performance, with primary education associated with lower scores. Additionally, sex was not found to be associated with performance. This study provides initial evidence supporting the validity and reliability of use of the Multiscent-20 as a digital odour identification test. The test's automation and portability enable the standardized delivery of olfactory stimuli and efficient automatic recording and scoring of responses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.N. participated as a medical consultant and received speaker fees from Noar Company. C.G. is CEO shareholder of the Noar Company, the manufacturer of the Noar MultiScent device described in this article. The remaining authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Kobal G, et al. Sniffin “Sticks”: Screening of olfactory performance. Rhinology. 1996;34:222–226. - PubMed
-
- Hummel T, Kobal G, Gudziol H, Mackay-Sim A. Normative data for the ‘Sniffin’’ Sticks” including tests of odor identification, odor discrimination, and olfactory thresholds: An upgrade based on a group of more than 3,000 subjects. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2007;264:237–243. doi: 10.1007/s00405-006-0173-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

