Reduction in ACE2 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells during COVID-19 - implications for post COVID-19 conditions
- PMID: 38956476
- PMCID: PMC11221185
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09321-0
Reduction in ACE2 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells during COVID-19 - implications for post COVID-19 conditions
Abstract
Background: Severe COVID-19 is uncommon, restricted to 19% of the total population. In response to the first virus wave (alpha variant of SARS-CoV-2), we investigated whether a biomarker indicated severity of disease and, in particular, if variable expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in blood might clarify this difference in risk and of post COVID -19 conditions (PCC).
Methods: The IRB-approved study compared patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 to healthy controls. Severe infection was defined requiring oxygen or increased oxygen need from baseline at admission with positive COVID-19 PCR. A single blood sample was obtained from patients within a day of admission. ACE2 RNA expression in blood cells was measured by an RT-PCR assay. Plasma ACE1 and ACE2 enzyme activities were quantified by fluorescent peptides. Plasma TIMP-1, PIIINP and MMP-9 antigens were quantified by ELISA. Data were entered into REDCap and analyzed using STATA v 14 and GraphPad Prism v 10.
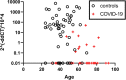
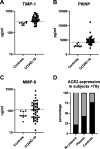
Results: Forty-eight patients and 72 healthy controls were recruited during the pandemic. ACE2 RNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) was rarely detected acutely during severe COVID-19 but common in controls (OR for undetected ACE2: 12.4 [95% CI: 2.62-76.1]). ACE2 RNA expression in PBMC did not determine plasma ACE1 and ACE2 activity, suggesting alternative cell-signaling pathways. Markers of fibrosis (TIMP-1 and PIIINP) and vasculopathy (MMP-9) were additionally elevated. ACE2 RNA expression during severe COVID-19 often responded within hours to convalescent plasma. Analogous to oncogenesis, we speculate that potent, persistent, cryptic processes following COVID-19 (the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), fibrosis and vasculopathy) initiate or promote post-COVID-19 conditions (PCC) in susceptible individuals.
Conclusions: This work elucidates biological and temporal plausibility for ACE2, TIMP1, PIIINP and MMP-9 in the pathogenesis of PCC. Intersection of these independent systems is uncommon and may in part explain the rarity of PCC.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; Transcription; COVID-19; Genetic; Leukocytes; Matrix metalloprotease-9; Mononuclear; Biomarkers; N-terminal peptide of procollagen III; Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome; Tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease-1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SNPs of ACE1 (rs4343) and ACE2 (rs2285666) genes are linked to SARS-CoV-2 infection but not with the severity of disease.Virol J. 2022 Mar 19;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01782-6. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 35305693 Free PMC article.
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 diabetes is associated with significant changes of ACE and ACE2 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022 May;32(5):1275-1282. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2022.01.029. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 35260304
-
Regulation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: A Potential Target to Prevent COVID-19?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 22;12:725967. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.725967. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34745001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACE2: from protection of liver disease to propagation of COVID-19.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Dec 11;134(23):3137-3158. doi: 10.1042/CS20201268. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33284956 Review.
Cited by
-
Scent of COVID-19: Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis Reveals the Role of ACE2, IFI44, and NDUFAF4 in Long-Lasting Olfactory Dysfunction.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 5;15(1):56. doi: 10.3390/life15010056. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39859996 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

