Comparison of microscopic and xpert MTB diagnoses of presumptive mycobacteria tuberculosis infection: retrospective analysis of routine diagnosis at Cape Coast Teaching Hospital
- PMID: 38956504
- PMCID: PMC11218342
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09566-9
Comparison of microscopic and xpert MTB diagnoses of presumptive mycobacteria tuberculosis infection: retrospective analysis of routine diagnosis at Cape Coast Teaching Hospital
Abstract
Introduction: Tuberculosis is a global health problem that causes 1. 4 million deaths every year. It has been estimated that sputum smear-negative diagnosis but culture-positive pulmonary TB diagnosis contribute to 12.6% of pulmonary TB transmission. TB diagnosis by smear microscopy smear has a minimum detection limit (LOD) of 5,000 to 10,000 bacilli per milliliter (CFU/ml) of sputum result in missed cases and false positives. However, GeneXpert technology, with a LOD of 131-250 CFU/ml in sputum samples and its implementation is believe to facilitate early detection TB and drug-resistant TB case. Since 2013, Ghana health Service (GHS) introduce GeneXpert MTB/RIF diagnostic in all regional hospitals in Ghana, however no assessment of performance between microscopy and GeneXpert TB diagnosis cross the health facilities has been reported. The study compared the results of routine diagnoses of TB by microscopy and Xpert MTB from 2016 to 2020 at the Cape Coast Teaching Hospital (CCTH).
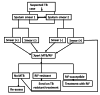
Methods: The study compared routine microscopic and GeneXpert TB diagnosis results at the Cape Coast Teaching Hospital (CCTH) from 2016 to 2020 retrospectively. Briefly, sputum specimens were collected into 20 mL sterile screw-capped containers for each case of suspected TB infection and processed within 24 h. The samples were decontaminated using the NALC-NaOH method with the final NaOH concentration of 1%. The supernatants were discarded after the centrifuge and the remaining pellets dissolved in 1-1.5 ml of phosphate buffer saline (PBS) and used for diagnosis. A fixed smears were Ziehl-Neelsen acid-fast stain and observed under microscope and the remainings were used for GeneXpert MTB/RIF diagnosis. The data were analyze using GraphPad Prism.
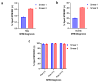
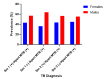
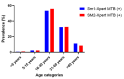
Results: 50.11% (48.48-51.38%) were females with an odd ratio (95% CI) of 1.004 (0.944-1.069) more likely to report to the TB clinic for suspected TB diagnosis. The smear-positive cases for the first sputum were 6.6% (5.98-7.25%), and the second sputum was 6.07% (5.45-6.73%). The Xpert MTB-RIF diagnosis detected 2.93% (10/341) (1.42-5.33%) in the first and 5.44% (16/294) (3.14-8.69%) in the second smear-negative TB samples. The prevalence of Xpert MTB-RIF across smear positive showed that males had 56.87% (178/313) and 56.15% (137/244) and females had 43.13% (135/313) and 43.85% (107/244) for the first and second sputum. Also, false negative smears were 0.18% (10/5607) for smear 1 and 0.31% (16/5126) for smear 2.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the study highlights the higher sensitivity of the GeneXpert assay compared to traditional smear microscopy for detecting MTB. The GeneXpert assay identified 10 and 16 positive MTB from smear 1 and smear 2 samples which were microscopic negative.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB); Cape Coast Teaching Hospital (CCTH); GeneXpert MTB/RIF; Ghana; TB diagnosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Xpert MTB/RIF assay for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in sputum specimens in remote health care facility.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Oct 19;15:220. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0566-6. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26483194 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in AFB smear-negative sputum specimens through MTB culture and GeneXpert® MTB/RIF assay.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2019 Jan-Dec;33:2058738419827174. doi: 10.1177/2058738419827174. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30791749 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic utility of GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay versus conventional methods for diagnosis of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis.BMC Microbiol. 2021 May 13;21(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02210-5. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33980173 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis to compare the accuracy of GeneXpert, MODS and the WHO 2007 algorithm for diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Oct 30;13:507. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-507. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24172543 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Simultaneous Tuberculosis and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Rifampicin Resistance: A Review of Diagnostic Accuracy [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2020 Dec 10. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2020 Dec 10. PMID: 33534447 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Xpert MTB/RIF assay in detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis in samples with different results by smear and culture in a coastal city with high incidence of tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 11;25(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10446-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39799307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soni NK, Bioactivity. Molecular Docking, and Pharmacophore Modeling of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A Study Targeting the Microarray Data of the Microbe. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutics (AJP). 2017;11(04).
-
- Dhingra S, Rahman NA, Peile E, Rahman M, Sartelli M, Hassali MA, Islam T, Islam S, Haque M. Microbial resistance movements: an overview of global public health threats posed by antimicrobial resistance, and how best to counter. Front Public Health. 2020;8:535668. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.535668. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

