Easily misdiagnosed X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 38956688
- PMCID: PMC11218101
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-024-01669-y
Easily misdiagnosed X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
Background: Addison's disease and X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) (Addison's-only) are two diseases that need to be identified. Addison's disease is easy to diagnose clinically when only skin and mucosal pigmentation symptoms are present. However, X-ALD (Addison's-only) caused by ABCD1 gene variation is ignored, thus losing the opportunity for early treatment. This study described two patients with initial clinical diagnosis of Addison's disease. However, they rapidly developed neurological symptoms triggered by infection. After further genetic testing, the two patients were diagnosed with X-ALD.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed X-ALD patients admitted to our hospital. Clinical features, laboratory test results, and imaging data were collected. Whole-exome sequencing was used in molecular genetics.
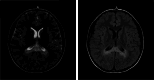
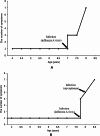
Results: Two patients were included in this study. Both of them had significantly increased adrenocorticotropic hormone level and skin and mucosal pigmentation. They were initially clinically diagnosed with Addison's disease and received hydrocortisone treatment. However, both patients developed progressive neurological symptoms following infectious disease. Further brain magnetic resonance imaging was completed, and the results suggested demyelinating lesions. Molecular genetics suggested variations in the ABCD1 gene, which were c.109_110insGCCA (p.C39Pfs*156), c.1394-2 A > C (NM_000033), respectively. Therefore, the two patients were finally diagnosed with X-ALD, whose classification had progressed from X-ALD (Addison's-only) to childhood cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (CCALD). Moreover, the infection exacerbates the demyelinating lesions and accelerates the onset of neurological symptoms. Neither the two variation sites in this study had been previously reported, which extends the ABCD1 variation spectrum.
Conclusions: Patients with only symptoms of adrenal insufficiency cannot be simply clinically diagnosed with Addison's disease. Being alert to the possibility of ABCD1 variation is necessary, and complete genetic testing is needed as soon as possible to identify X-ALD (Addison's-only) early to achieve regular monitoring of the disease and receive treatment early. In addition, infection, as a hit factor, may aggravate demyelinating lesions of CCALD. Thus, patients should be protected from external environmental factors to delay the progression of cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy.
Keywords: ABCD1; Addison; Adrenoleukodystrophy; Hit; Infection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

