RNA sequencing reveals the potential mechanism of exercise preconditioning for cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats
- PMID: 38956886
- PMCID: PMC11219470
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.3608
RNA sequencing reveals the potential mechanism of exercise preconditioning for cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
Introduction: Cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury (CIRI) often leads to deleterious complications after stroke patients receive reperfusion therapy. Exercise preconditioning (EP) has been reported to facilitate brain function recovery. We aim to explore the specific mechanism of EP in CIRI.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were randomized into Sham, middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), and EP groups (n = 11). The rats in the EP group received adaptive training for 3 days (10 m/min, 20 min/day, with a 0° incline) and formal training for 3 weeks (6 days/week, 25 m/min, 30 min/day, with a 0° incline). Then, rats underwent MCAO surgery to establish CIRI models. After 48 h, neurological deficits and cerebral infarction of the rats were measured. Neuronal death and apoptosis in the cerebral cortices were detected. Furthermore, RNA sequencing was conducted to investigate the specific mechanism of EP on CIRI, and qPCR and Western blotting were further applied to confirm RNA sequencing results.
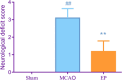
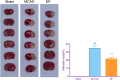
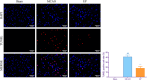
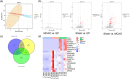
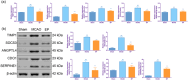
Results: EP improved neurological deficit scores and reduced cerebral infarction in MCAO rats. Additionally, pre-ischemic exercise also alleviated neuronal death and apoptosis of the cerebral cortices in MCAO rats. Importantly, 17 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified through RNA sequencing, and these DEGs were mainly enriched in the HIF-1 pathway, cellular senescence, proteoglycans in cancer, and so on. qPCR and Western blotting further confirmed that EP could suppress TIMP1, SOCS3, ANGPTL4, CDO1, and SERPINE1 expressions in MCAO rats.
Conclusion: EP can improve CIRI in vivo, the mechanism may relate to TIMP1 expression and HIF-1 pathway, which provided novel targets for CIRI treatment.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; TIMP1/HIF‐1 pathway; cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury; exercise preconditioning.
© 2024 The Author(s). Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exercise preconditioning mitigates brain injury after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by restraining TIMP1.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Oct;12(10):e70008. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70008. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39364701 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed genes induced by β-caryophyllene in a rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Life Sci. 2021 May 15;273:119293. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119293. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33705733
-
Sanpian decoction ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating SIRT1/ERK/HIF-1α pathway through in silico analysis and experimental validation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt A):116898. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116898. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37467820
-
Exercise preconditioning increases circulating exosome miR-124 expression and alleviates apoptosis in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Brain Res. 2025 Mar 15;1851:149457. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2025.149457. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39824375
-
Exercise preconditioning reduces ischemia reperfusion-induced focal cerebral infarct volume through up-regulating the expression of HIF-1α.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015 Mar;28(2 Suppl):791-8. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25796156
Cited by
-
Assessment of the Impact of Sensor-Based Ischemic Preconditioning with Different Cycling Periods on Upper Limb Strength in Bodybuilding Athletes.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 13;24(18):5943. doi: 10.3390/s24185943. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338688 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Arabzadeh, E. , Norouzi Kamareh, M. , Ramirez‐Campillo, R. , Mirnejad, R. , Masti, Y. , & Shirvani, H. (2022). Twelve weeks of treadmill exercise training with green tea extract reduces myocardial oxidative stress and alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis in aging rat: The emerging role of BNIP3 and HIF‐1α/IGFBP3 pathway. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 46(12), e14397. 10.1111/jfbc.14397 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

