Pharmacological effects of bioactive agents in earthworm extract: A comprehensive review
- PMID: 38957072
- PMCID: PMC11528390
- DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12465
Pharmacological effects of bioactive agents in earthworm extract: A comprehensive review
Abstract
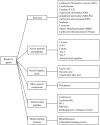
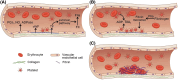
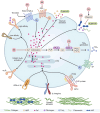
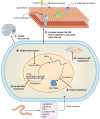
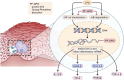
This review compiles information from the literature on the chemical composition, pharmacological effects, and molecular mechanisms of earthworm extract (EE) and suggests possibilities for clinical translation of EE. We also consider future trends and concerns in this domain. We summarize the bioactive components of EE, including G-90, lysenin, lumbrokinase, antimicrobial peptides, earthworm serine protease (ESP), and polyphenols, and detail the antitumor, antithrombotic, antiviral, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxidant, wound-healing, antifibrotic, and hypoglycemic activities and mechanisms of action of EE based on existing in vitro and in vivo studies. We further propose the potential of EE for clinical translation in anticancer and lipid-modifying therapies, and its promise as source of a novel agent for wound healing and resistance to antibiotic tolerance. The earthworm enzyme lumbrokinase embodies highly effective anticoagulant and thrombolytic properties and has the advantage of not causing bleeding phenomena due to hyperfibrinolysis. Its antifibrotic properties can reduce the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix. The glycolipoprotein extract G-90 can effectively scavenge reactive oxygen groups and protect cellular tissues from oxidative damage. Earthworms have evolved a well-developed defense mechanism to fight against microbial infections, and the bioactive agents in EE have shown good antibacterial, fungal, and viral properties in in vitro and in vivo experiments and can alleviate inflammatory responses caused by infections, effectively reducing pain. Recent studies have also highlighted the role of EE in lowering blood glucose. EE shows high medicinal value and is expected to be a source of many bioactive compounds.
Keywords: antithrombotic; antitumor; bioactive agent; earthworm extract; pharmacological effects.
© 2024 The Author(s). Animal Models and Experimental Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Chinese Association for Laboratory Animal Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Xin T, Zhang Y, Pu X, Gao R, Xu Z, Song J. Trends in herbgenomics. Sci China Life Sci. 2019;62(3):288‐308. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, Chen S, Cai J, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine syndrome‐related herbal prescriptions in treatment of malignant tumors. J Trad Chin Med. 2013;33(1):19‐26. - PubMed
-
- Fu Z, Zhang L, Liu X, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of the sun‐ and freeze‐dried earthworm Eisenia fetida with differentially thrombolytic activities. J Proteome. 2013;83:1‐14. - PubMed
-
- Gu Y, Zhang J, Sun J, et al. Marker peptide screening and species‐specific authentication of Pheretima using proteomics. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413(12):3167‐3176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

