Comparative study of immune response to local tumor destruction modalities in a murine breast cancer model
- PMID: 38957315
- PMCID: PMC11217310
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1405486
Comparative study of immune response to local tumor destruction modalities in a murine breast cancer model
Abstract
Introduction: Immunotherapy is revolutionizing the management of multiple cancer types. However, only a subset of patients responds to immunotherapy. One mechanism of resistance is the absence of immune infiltrates within the tumor. In situ vaccine with local means of tumor destruction that can induce immunogenic cell death have been shown to enhance tumor T cell infiltration and increase efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade.
Methods: Here, we compare three different forms of localize tumor destruction therapies: radiation therapy (RT), vascular targeted photodynamic therapy (VTP) and cryoablation (Cryo), which are known to induce immunogenic cell death, with their ability to induce local and systemic immune responses in a mouse 4T1 breast cancer model. The effects of combining RT, VTP, Cryo with anti-PD1 was also assessed.
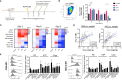
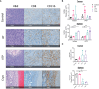
Results: We observed that RT, VTP and Cryo significantly delayed tumor growth and extended overall survival. In addition, they also induced regression of non-treated distant tumors in a bilateral model suggesting a systemic immune response. Flow cytometry showed that VTP and Cryo are associated with a reduction in CD11b+ myeloid cells (granulocytes, monocytes, and macrophages) in tumor and periphery. An increase in CD8+ T cell infiltration into tumors was observed only in the RT group. VTP and Cryo were associated with an increase in CD4+ and CD8+ cells in the periphery.
Conclusion: These data suggest that cell death induced by VTP and Cryo elicit similar immune responses that differ from local RT.
Keywords: breast cancer; cryoablation; immune checkpoint blockade; radiation therapy; vascular photodynamic therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Budhu, Kim, Yip, La Rosa, Jebiwott, Cai, Holland, Thomas, Preise, Somma, Gordon, Scherz, Wolchok, Erinjeri, Merghoub and Coleman.
Conflict of interest statement
TM is a consultant for Immunos Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo Co, TigaTx, Normunity and Pfizer; is a cofounder of and equity holder in IMVAQ Therapeutics; receives research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Realta; is an inventor on patent applications related to work on oncolytic viral therapy, alpha virus–based vaccine, neo antigen modeling, CD40, GITR, OX40, PD-1, and CTLA-4. JW is a consultant for: Apricity; Ascentage Pharma; AstraZeneca; BeiGene; Bicara Therapeutics; Bristol Myers Squibb; Daiichi Sankyo; Dragonfly; Imvaq; Larkspur; Takeda; Tizona; Trishula Therapeutics; Immunocore is on their Data Safety board. JW received Grant/Research Support from: Bristol Myers Squibb; Enterome. JW has Equity in: Apricity, Arsenal IO/CellCarta; Ascentage; Imvaq; Linneaus, Larkspur; Georgiamune; Maverick; Tizona Therapeutics; Xenimmune. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

