The monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio at diagnosis is associated with cerebrovascular accident during follow-up in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis
- PMID: 38957360
- PMCID: PMC11215250
- DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2024.0001
The monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio at diagnosis is associated with cerebrovascular accident during follow-up in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis
Abstract
Objective: In this study, the association between the monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (MHR) at diagnosis and poor outcomes of atherosclerosis-related antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV) during follow-up in patients with AAV was investigated.
Methods: This retrospective study included 138 patients diagnosed with AAV. Their comprehensive medical records were meticulously reviewed. All-cause mortality, cerebrovascular accident (CVA), and acute coronary syndrome (ACS) were evaluated as atherosclerosis-related poor outcomes of AAV. MHR was obtained by dividing monocyte counts (/mm3) by high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mg/dL) levels.
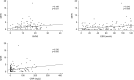
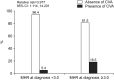
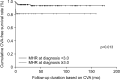
Results: The median age of the 138 patients was 58.3 years with 44 being male (31.9%). Among the 138 patients, 11 (8.0%) died, and 11 (8.0%) and 9 (6.5%) had CVA, and ACS, respectively. MHR at diagnosis was significantly correlated with the Birmingham vasculitis activity score, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein at diagnosis. Among the three poor outcomes of AAV, only CVA during follow-up was significantly associated with MHR at diagnosis, and thus, only CVA was considered an atherosclerosis-related poor outcome of AAV. In the multivariable Cox hazards model analysis, MHR (hazard ratio [HR] 1.195) and serum albumin (HR 0.203) at diagnosis were independently associated with CVA during follow-up. Additionally, patients with MHR at diagnosis ≥3.0 exhibited a significantly higher risk for CVA and lower cumulative CVA-free survival rate than those with MHR at diagnosis <3.0.
Conclusion: This study is the first to demonstrate clinical implications of MHR suggesting that MHR at diagnosis is significantly and independently associated with CVA during follow-up in patients with AAV.
Keywords: Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; High density lipoprotein cholesterol; Monocytes; Stroke; Vasculitis.
Copyright © 2024 by The Korean College of Rheumatology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atherogenic index of plasma predicts cerebrovascular accident occurrence in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Aug 14;19(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01360-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32799861 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive potential of albumin-alkaline phosphatase ratio for cerebrovascular accident in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.Ann Clin Biochem. 2023 May;60(3):184-190. doi: 10.1177/00045632231154752. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Ann Clin Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36653311
-
Male Sex Is a Significant Predictor of All-cause Mortality in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated Vasculitis.J Korean Med Sci. 2021 May 10;36(18):e120. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e120. J Korean Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33975396 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Liver Index Independently Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis but No Substantial Liver Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 23;9:848121. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.848121. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35811721 Free PMC article.
-
Stroke Is Not an Accident: An Integrative Review on the Use of the Term Cerebrovascular Accident.Neuroepidemiology. 2024 Oct 28:1-9. doi: 10.1159/000542301. Online ahead of print. Neuroepidemiology. 2024. PMID: 39467531 Review.
References
-
- Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, et al. Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:222–7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.054593. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
