Neurovascular coupling, functional connectivity, and cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 38958537
- PMCID: PMC11350141
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14072
Neurovascular coupling, functional connectivity, and cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
Introduction: Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a prodromal stage of dementia. Understanding the mechanistic changes from healthy aging to MCI is critical for comprehending disease progression and enabling preventative intervention.
Methods: Patients with MCI and age-matched controls (CN) were administered cognitive tasks during functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) recording, and changes in plasma levels of extracellular vesicles (EVs) were assessed using small-particle flow cytometry.
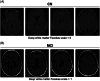
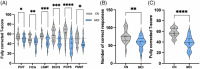
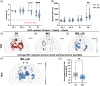
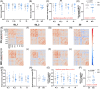
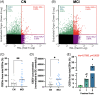
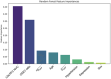
Results: Neurovascular coupling (NVC) and functional connectivity (FC) were decreased in MCI compared to CN, prominently in the left-dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (LDLPFC). We observed an increased ratio of cerebrovascular endothelial EVs (CEEVs) to total endothelial EVs in patients with MCI compared to CN, correlating with structural MRI small vessel ischemic damage in MCI. LDLPFC NVC, CEEV ratio, and LDLPFC FC had the highest feature importance in the random Forest group classification.
Discussion: NVC, CEEVs, and FC predict MCI diagnosis, indicating their potential as markers for MCI cerebrovascular pathology.
Highlights: Neurovascular coupling (NVC) is impaired in mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Functional connectivity (FC) compensation mechanism is lost in MCI. Cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles (CEEVs) are increased in MCI. CEEV load strongly associates with cerebral small vessel ischemic lesions in MCI. NVC, CEEVs, and FC predict MCI diagnosis over demographic and comorbidity factors.
Keywords: endothelium; extracellular vesicles; functional connectivity; mild cognitive impairment; neurovascular coupling.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01 CX000340/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- I01 CX002578/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- AHA932980/The American Heart Association
- K01 AG073613/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD109157/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG055395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CX000340/U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs
- T32 AG052363/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068295/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG072295/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA255840/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS085002/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32AG052363/NIA-funded Geroscience Training Program in Oklahoma
- K01 AG073614/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1NS085002/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG072295/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104938/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX006026/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- IK2 CX002180/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- 932980/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R03 AG070479/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG055395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075834/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54GM104938/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03AG070479/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD109157/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- K01AG073614/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CX002578/U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs
- R01AG068295/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS100782/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA255840/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG080775/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 23DIVSUP1070991/The American Heart Association
- P30 AG066514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG075834/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 966924/The American Heart Association
- AHA941290/The American Heart Association
- K01AG073613/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS100782/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG080775/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Oklahoma Shared Clinical and Translational Resources (OSCTR)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

