Sex ratio and age of onset in AQP4 antibody-associated NMOSD: a review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38958756
- PMCID: PMC11319503
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-024-12452-8
Sex ratio and age of onset in AQP4 antibody-associated NMOSD: a review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody-associated neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is an antibody-mediated inflammatory disease of the central nervous system. We have undertaken a systematic review and meta-analysis to ascertain the sex ratio and mean age of onset for AQP4 antibody associated NMOSD. We have also explored factors that impact on these demographic data.
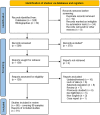
Methods: A systematic search of databases was conducted according to the PRISMA guidelines. Articles reporting sex distribution and age of onset for AQP4 antibody-associated NMSOD were reviewed. An initially inclusive approach involving exploration with regression meta-analysis was followed by an analysis of just AQP4 antibody positive cases.
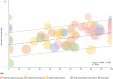
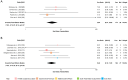
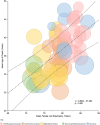
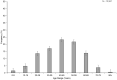
Results: A total of 528 articles were screened to yield 89 articles covering 19,415 individuals from 88 population samples. The female:male sex ratio was significantly influenced by the proportion of AQP4 antibody positive cases in the samples studied (p < 0.001). For AQP4 antibody-positive cases the overall estimate of the sex ratio was 8.89 (95% CI 7.78-10.15). For paediatric populations the estimate was 5.68 (95% CI 4.01-8.03) and for late-onset cases, it was 5.48 (95% CI 4.10-7.33). The mean age of onset was significantly associated with the mean life expectancy of the population sampled (p < 0.001). The mean age of onset for AQP4 antibody-positive cases in long-lived populations was 41.7 years versus 33.3 years in the remainder.
Conclusions: The female:male sex ratio and the mean age of onset of AQP4 antibody-associated NMOSD are significantly higher than MS. The sex ratio increases with the proportion of cases that are positive for AQP4 antibodies and the mean age of onset increases with population life expectancy.
Keywords: Aetiology; Age of onset; Environment; Epidemiology; Neuromyelitis optica; Risk factors; Sex.
© 2024. Crown.
Conflict of interest statement
SA, SHC, UL, JYH, GA, VEN, JQ, EM, JS and NA declare no conflicts of interest. FP has received research support from DFG, BMBF, KKNMS, and the Guthy-Jackson Charitable Foundation. He serves on steering committees of the OCTIMS study (Novartis) and the N-Momentum study (Viela Bio) and has received personal compensation and research support from Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, Roche, Merck, Teva, Shire, Celgene, Novartis, and Sanofi Genzyme. He is an associate editor of Neurology: Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation. MRY is the founder of NovaDigm Therapeutics, Inc, and Metacin, Inc. He is a member of the Genentech Scientific Advisory Committee and has received travel expenses or honoraria from Genentech and Alexion. ML has had roles as a pharmaceutical consultant for Alexion, Chugai, Horizon, Roche, Genzyme, UCB, and Quest Diagnostics, and has received grants from Alexion, Shire, Horizon, Genzyme, Sanofi, UCB. BGW has received royalties from RSR Ltd, Oxford University, Hospices Civil de Lyon, and MVZ Labor PD Dr. Volkmann und Kollegen GbR for a patent of NMO-IgG as a diagnostic test for NMO and related disorders, served on adjudication committee for clinical trials in NMO being conducted by MedImmune and Alexion, and consulted for Chugai, Mitsubishi-Tanabe regarding a clinical trial for NMO. BLB has received personal fees from Novartis. KF has received grants from Ministry of Education, Science and Technology of Japan and the Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Labor of Japan, and received honoraria, and/or travel expenses for speaking, and/or advisory boards from Mitsubishi Tanabe, Biogen, Bayer, Takeda, Novartis, Alexion, VielaBio, Asahi Kasei, Dainihon Sumitomo, Eisai, Teijin, Ono, Roche, and Chugai. H. Abboud has received consultancy and speaker fees from Biogen, Genentech-Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Alexion, and Horizon, and has received research support from Genentech-Roche, Novartis, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Bristol Myers Squibb to conduct clinical trials. IDB has been a site Principal Investigator in clinical trials and projects sponsored by Alexion Pharmaceuticals/Astra Zeneca and CorEvitas, has received travel reimbursement from The Guthy-Jackson Charitable Foundation, is a member of The Guthy-Jackson Charitable Foundation International Clinical Consortium; and received grant support from The Bodford Family Transverse Myelitis Center Research Fund. JP has received support for scientific meetings and honorariums for advisory work from Merck-Serono, Sandoz, Sanofi, Novartis, Chugai, Alexion, Clene, Roche, Medimmune, Amgen, Vitaccess, UCB, Mitsubishi, Amplo and Janssen. Grants from Alexion, Argenx, Roche, Medimmune, UCB and Amplo biotechnology. Patent ref P37347WO and license agreement Numares multimarker MS diagnostics. Has shares in AstraZenica. SAB has received honoraria for attendance at advisory boards and travel sponsorship from Biogen-Idec, Merck-Serono, Novartis and Sanofi-Genzyme; has received speakers honoraria from Biogen-Idec and Genzyme; is an investigator in clinical trials sponsored by Biogen Idec and Novartis.
Figures


References
-
- Wingerchuk DM, Banwell B, Bennett JL, Cabre P, Carroll W, Chitnis T, de Seze J, Fujihara K, Greenberg B, Jacob A, Jarius S, Lana-Peixoto M, Levy M, Simon JH, Tenembaum S, Traboulsee AL, Waters P, Wellik KE, Weinshenker BG, International Panel for NMOD (2015) International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 85(2):177–189. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001729 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001729 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santos E, Rocha AL, Oliveira V, Ferro D, Samoes R, Sousa AP, Figueiroa S, Mendonca T, Abreu P, Guimaraes J, Sousa R, Melo C, Correia I, Duraes J, Sousa L, Ferreira J, de Sa J, Sousa F, Sequeira M, Correia AS, Andre AL, Basilio C, Arenga M, Mendes I, Marques IB, Perdigao S, Felgueiras H, Alves I, Correia F, Barroso C, Morganho A, Carmona C, Palavra F, Santos M, Salgado V, Palos A, Nzwalo H, Timoteo A, Guerreiro R, Isidoro L, Boleixa D, Carneiro P, Neves E, Silva AM, Goncalves G, Leite MI, Sa MJ (2021) Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: a nationwide Portuguese clinical epidemiological study. Mult Scler Relat Disord 56:103258. 10.1016/j.msard.2021.103258 10.1016/j.msard.2021.103258 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Watanabe M, Nakamura Y, Sato S, Niino M, Fukaura H, Tanaka M, Ochi H, Kanda T, Takeshita Y, Yokota T, Nishida Y, Matsui M, Nagayama S, Kusunoki S, Miyamoto K, Mizuno M, Kawachi I, Saji E, Ohashi T, Shimohama S, Hisahara S, Nishiyama K, Iizuka T, Nakatsuji Y, Okuno T, Ochi K, Suzumura A, Yamamoto K, Kawano Y, Tsuji S, Hirata M, Sakate R, Kimura T, Shimizu Y, Nagaishi A, Okada K, Hayashi F, Sakoda A, Masaki K, Shinoda K, Isobe N, Matsushita T, Kira JI (2021) HLA genotype-clinical phenotype correlations in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders based on Japan MS/NMOSD Biobank data. Sci Rep 11(1):607. 10.1038/s41598-020-79833-7 10.1038/s41598-020-79833-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

