The Role of Physical Exercise as a Therapeutic Tool to Improve Lipedema: A Consensus Statement from the Italian Society of Motor and Sports Sciences (Società Italiana di Scienze Motorie e Sportive, SISMeS) and the Italian Society of Phlebology (Società Italiana di Flebologia, SIF)
- PMID: 38958868
- PMCID: PMC11522091
- DOI: 10.1007/s13679-024-00579-8
The Role of Physical Exercise as a Therapeutic Tool to Improve Lipedema: A Consensus Statement from the Italian Society of Motor and Sports Sciences (Società Italiana di Scienze Motorie e Sportive, SISMeS) and the Italian Society of Phlebology (Società Italiana di Flebologia, SIF)
Abstract
Purpose of review: This consensus statement from the Italian Society of Motor and Sports Sciences (Società Italiana di Scienze Motorie e Sportive, SISMeS) and the Italian Society of Phlebology (Società Italiana di Flebologia, SIF) provides the official view on the role of exercise as a non-pharmacological approach in lipedema. In detail, this consensus statement SISMeS - SIF aims to provide a comprehensive overview of lipedema, focusing, in particular, on the role played by physical exercise (PE) in the management of its clinical features.
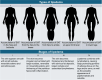
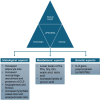
Recent findings: Lipedema is a chronic disease characterized by abnormal fat accumulation. It is often misdiagnosed as obesity, despite presenting distinct pathological mechanisms. Indeed, recent evidence has reported differences in adipose tissue histology, metabolomic profiles, and gene polymorphisms associated with this condition, adding new pieces to the complex puzzle of lipedema pathophysiology. Although by definition lipedema is a condition resistant to diet and PE, the latter emerges for its key role in the management of lipedema, contributing to multiple benefits, including improvements in mitochondrial function, lymphatic drainage, and reduction of inflammation. Various types of exercise, such as aquatic exercises and strength training, have been shown to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life of patients with lipedema. However, standardized guidelines for PE prescription and long-term management of patients with lipedema are lacking, highlighting the need for recommendations and further research in this area in order to optimise therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: BMI; Hormones; Lipedema; Obesity; Physical activity; Sport.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Allen E, Hines E, Hines E. Lipedema of the legs: A syndrome characterized by fat legs and orthostatic edema. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1940;15:184–7.
-
- Verde L, Camajani E, Annunziata G, Sojat A, Marina L, Colao A, et al. Ketogenic diet: A nutritional therapeutic tool for lipedema? Curr Obes Rep. 2023;12:529–43. Due to its anti-inflammatory and fat mass-reducing effects, VLCKD may be considered as an effective dietary treatment for lipedema, in particular in the context of obesity. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Felmerer G, Stylianaki A, Hägerling R, et al. Adipose tissue hypertrophy, an aberrant biochemical profile and distinct gene expression in lipedema. J Surg Res. 2020;253:294–303. - PubMed
-
- Hardy D, Williams A. Best practice guidelines for the management of lipedema. Br J Community Nurs. 2017;22:S44–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

