Tamoxifen may contribute to preserve cardiac function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 38960907
- PMCID: PMC11322393
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-024-05670-9
Tamoxifen may contribute to preserve cardiac function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
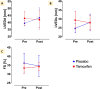
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is life-limiting. Cardiomyopathy, which mostly ensues in the second decade of life, is the main cause of death. Treatment options are still limited. The TAMDMD (NCT03354039) trial assessed motor function, muscle strength and structure, laboratory biomarkers, and safety in 79 ambulant boys with genetically confirmed Duchenne muscular dystrophy, 6.5-12 years of age, receiving either daily tamoxifen 20 mg or placebo for 48 weeks. In this post-hoc analysis, available echocardiographic data of ambulant patients recruited at one study centre were retrieved and compared before and after treatment. Data from 14 patients, median 11 (interquartile range, IQR, 11-12) years of age was available. Baseline demographic characteristics were similar in participants assigned to placebo (n = 7) or tamoxifen (n = 7). Left ventricular end-diastolic diameter in the placebo group (median and IQR) was 39 (38-41) mm at baseline and 43 (38-44) mm at study end, while it was 44 (41-46) mm at baseline and 41 (37-46) mm after treatment in the tamoxifen group. Left ventricular fractional shortening in the placebo group was 35% (32-38%) before and 33% (32-36%) after treatment, while in the tamoxifen group it was 34% (33-34%) at baseline and 35% (33-35%) at study end. No safety signals were detected.
Conclusion: This hypothesis-generating post-hoc analysis suggests that tamoxifen over 48 weeks is well tolerated and may help preserving cardiac structure and function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Further studies are justified.
Clinicaltrials: gov Identifier: EudraCT 2017-004554-42, NCT03354039 What is known: • Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is life-limiting. Cardiomyopathy ensues in the second decade of life and is the main cause of death. Treatment options are still limited. • Tamoxifen reduced cardiac fibrosis in mice and improved cardiomyocyte function in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.
What is new: • In this post-hoc analysis of the TAMDMD trial among 14 boys, median 11 years of age, treated with either tamoxifen or placebo for 48 weeks, treatment was well-tolerated. • A visual trend of improved left-ventricular dimensions and better systolic function preservation generates the hypothesis of a potential beneficial effect of tamoxifen in DMD cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy; Dilated cardiomyopathy; Duchenne muscular dystrophy; Heart failure; Tamoxifen.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Birnkrant DJ, Bushby K, Bann CM, Apkon SD, Blackwell A, Brumbaugh D et al (2018) Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and neuromuscular, rehabilitation, endocrine, and gastrointestinal and nutritional management. Lancet Neurol 17(3):251–267 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30024-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birnkrant DJ, Bushby K, Bann CM, Apkon SD, Blackwell A, Colvin MK et al (2018) Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 3: primary care, emergency management, psychosocial care, and transitions of care across the lifespan. Lancet Neurol 17(5):445–455 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30026-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

