The emerging role of nuclear receptor coactivator 4 in health and disease: a novel bridge between iron metabolism and immunity
- PMID: 38961066
- PMCID: PMC11222541
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-024-02075-3
The emerging role of nuclear receptor coactivator 4 in health and disease: a novel bridge between iron metabolism and immunity
Abstract
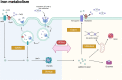
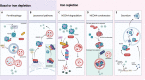
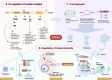
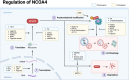
Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) has recently been recognized as a selective cargo receptor of ferritinophagy participating in ferroptosis. However, NCOA4 is also a coactivator that modulates the transcriptional activity of many vital nuclear receptors. Recent novel studies have documented the role of NCOA4 in healthy and pathogenic conditions via its modulation of iron- and non-iron-dependent metabolic pathways. NCOA4 exhibits non-ferritinophagic and iron-independent features such as promoting tumorigenesis and erythropoiesis, immunomodulation, regulating autophagy, and participating in DNA replication and mitosis. Full-length human-NCOA4 is composed of 614 amino acids, of which the N-terminal (1-237) contains nuclear-receptor-binding domains, while the C-terminal (238-614) principally contains a ferritin-binding domain. The exploration of the protein structure of NCOA4 suggests that NCOA4 possesses additional significant and complex functions based on its structural domains. Intriguingly, another three isoforms of NCOA4 that are produced by alternative splicing have been identified, which may also display disparate activities in physiological and pathological processes. Thus, NCOA4 has become an important bridge that encompasses interactions between immunity and metabolism. In this review, we outline the latest advances in the important regulating mechanisms underlying NCOA4 actions in health and disease conditions, providing insights into potential therapeutic interventions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy in Ferroptosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1301:41-57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-62026-4_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34370287 Review.
-
The Role of NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy in Health and Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018 Oct 23;11(4):114. doi: 10.3390/ph11040114. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30360520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and characterization of the ferritin binding domain of Nuclear Receptor Coactivator-4 (NCOA4).Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Nov;1861(11 Pt A):2710-2716. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.07.015. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28754384
-
Ferritinophagy via NCOA4 is required for erythropoiesis and is regulated by iron dependent HERC2-mediated proteolysis.Elife. 2015 Oct 5;4:e10308. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10308. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26436293 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 signaling promotes cardiac injury by upregulating NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in high-fat-diet fed mice.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 May 20;201:111-125. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.003. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36940731
Cited by
-
Potential applications of gene expression profiles obtained from circulating extracellular vesicles in breast cancer.J Liq Biopsy. 2025 Jan 19;7:100287. doi: 10.1016/j.jlb.2025.100287. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Liq Biopsy. 2025. PMID: 40027231 Free PMC article.
-
Ferritinophagy: a possible new iron-related metabolic target in canine osteoblastic osteosarcoma.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 24;12:1546872. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1546872. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40196812 Free PMC article.
-
Toosendanin induces ferroptosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells through the regulation of the NCOA4 ferritinophagy pathway: implications for tumor proliferation, migration, and invasion.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Jun 30;16(3):853-864. doi: 10.21037/jgo-2024-1002. Epub 2025 Jun 26. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40672075 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics and experimental validation of ferroptosis-related genes in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 12;12:1578755. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1578755. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40421419 Free PMC article.
-
Second-generation BRAF inhibitor Encorafenib resistance is regulated by NCOA4-mediated iron trafficking in the drug-resistant malignant melanoma cells.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 18;15(1):2422. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86874-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39827294 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

