A(H2N2) and A(H3N2) influenza pandemics elicited durable cross-reactive and protective antibodies against avian N2 neuraminidases
- PMID: 38961067
- PMCID: PMC11222539
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49884-9
A(H2N2) and A(H3N2) influenza pandemics elicited durable cross-reactive and protective antibodies against avian N2 neuraminidases
Abstract
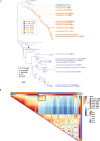
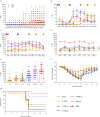
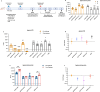
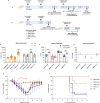
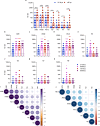
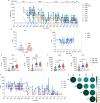
Human cases of avian influenza virus (AIV) infections are associated with an age-specific disease burden. As the influenza virus N2 neuraminidase (NA) gene was introduced from avian sources during the 1957 pandemic, we investigate the reactivity of N2 antibodies against A(H9N2) AIVs. Serosurvey of healthy individuals reveal the highest rates of AIV N2 antibodies in individuals aged ≥65 years. Exposure to the 1968 pandemic N2, but not recent N2, protected against A(H9N2) AIV challenge in female mice. In some older adults, infection with contemporary A(H3N2) virus could recall cross-reactive AIV NA antibodies, showing discernable human- or avian-NA type reactivity. Individuals born before 1957 have higher anti-AIV N2 titers compared to those born between 1957 and 1968. The anti-AIV N2 antibodies titers correlate with antibody titers to the 1957 N2, suggesting that exposure to the A(H2N2) virus contribute to this reactivity. These findings underscore the critical role of neuraminidase immunity in zoonotic and pandemic influenza risk assessment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
B.J.C. has consulted for AstraZeneca, Fosun Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Haleon, Moderna, Novavax, Pfizer, Roche, and Sanofi Pasteur. S.S.W. has received speakers honorarium from Sanofi Pasteur. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 06-410-2106092/Guangzhou Medical University (Guangzhou Medical College)
- BT/IN/EU-INF/15/RV/19-20/Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology (DBT)
- 75N93021C00016/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 17114023/Research Grants Council, University Grants Committee (RGC, UGC)
- 06-410-2106093/Guangzhou Medical University (Guangzhou Medical College)
- HKU SRFS2021-7S03/Research Grants Council, University Grants Committee (RGC, UGC)
- 75N93021C00015/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T11-712/19-N/Research Grants Council, University Grants Committee (RGC, UGC)
- HHSD2002013M53890B (Subcontract 200-2014-F-60406) and cooperative agreement (grant no. 1U01IP001064)/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- U01IP001064/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- InnoHK/Innovation and Technology Commission (ITF)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

