Structure focused neurodegeneration convolutional neural network for modelling and classification of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38961114
- PMCID: PMC11222499
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-60611-8
Structure focused neurodegeneration convolutional neural network for modelling and classification of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
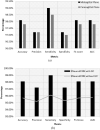
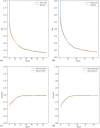
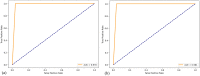
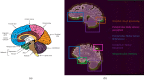
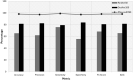
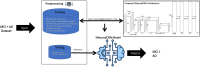
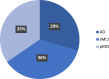
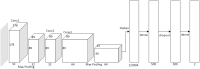
Alzheimer's disease (AD), the predominant form of dementia, is a growing global challenge, emphasizing the urgent need for accurate and early diagnosis. Current clinical diagnoses rely on radiologist expert interpretation, which is prone to human error. Deep learning has thus far shown promise for early AD diagnosis. However, existing methods often overlook focal structural atrophy critical for enhanced understanding of the cerebral cortex neurodegeneration. This paper proposes a deep learning framework that includes a novel structure-focused neurodegeneration CNN architecture named SNeurodCNN and an image brightness enhancement preprocessor using gamma correction. The SNeurodCNN architecture takes as input the focal structural atrophy features resulting from segmentation of brain structures captured through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). As a result, the architecture considers only necessary CNN components, which comprises of two downsampling convolutional blocks and two fully connected layers, for achieving the desired classification task, and utilises regularisation techniques to regularise learnable parameters. Leveraging mid-sagittal and para-sagittal brain image viewpoints from the Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI) dataset, our framework demonstrated exceptional performance. The para-sagittal viewpoint achieved 97.8% accuracy, 97.0% specificity, and 98.5% sensitivity, while the mid-sagittal viewpoint offered deeper insights with 98.1% accuracy, 97.2% specificity, and 99.0% sensitivity. Model analysis revealed the ability of SNeurodCNN to capture the structural dynamics of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and AD in the frontal lobe, occipital lobe, cerebellum, temporal, and parietal lobe, suggesting its potential as a brain structural change digi-biomarker for early AD diagnosis. This work can be reproduced using code we made available on GitHub.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Classification; Convolutional neural network; Deep learning; Mild cognitive impairment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A multi-model deep convolutional neural network for automatic hippocampus segmentation and classification in Alzheimer's disease.Neuroimage. 2020 Mar;208:116459. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116459. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 31837471
-
An intelligent magnetic resonance imagining-based multistage Alzheimer's disease classification using swish-convolutional neural networks.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025 Mar;63(3):885-899. doi: 10.1007/s11517-024-03237-2. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025. PMID: 39546213
-
A Deep Learning Approach for Automated Diagnosis and Multi-Class Classification of Alzheimer's Disease Stages Using Resting-State fMRI and Residual Neural Networks.J Med Syst. 2019 Dec 18;44(2):37. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1475-2. J Med Syst. 2019. PMID: 31853655
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
-
[Research on the application of convolution neural network in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Feb 25;38(1):169-177. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202007019. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33899442 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing diagnosis of pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on CT: a systematic review of imaging analysis through deep learning.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 8;15:1510026. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1510026. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39845042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association 2018 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dementia. 2018;14(3):367–429. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

