Integrative network analysis of miRNA-mRNA expression profiles during epileptogenesis in rats reveals therapeutic targets after emergence of first spontaneous seizure
- PMID: 38961125
- PMCID: PMC11222454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66117-7
Integrative network analysis of miRNA-mRNA expression profiles during epileptogenesis in rats reveals therapeutic targets after emergence of first spontaneous seizure
Abstract
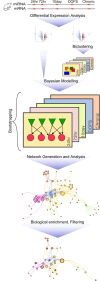
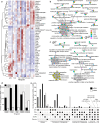
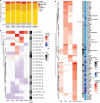
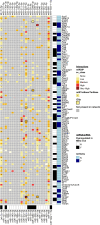
Epileptogenesis is the process by which a normal brain becomes hyperexcitable and capable of generating spontaneous recurrent seizures. The extensive dysregulation of gene expression associated with epileptogenesis is shaped, in part, by microRNAs (miRNAs) - short, non-coding RNAs that negatively regulate protein levels. Functional miRNA-mediated regulation can, however, be difficult to elucidate due to the complexity of miRNA-mRNA interactions. Here, we integrated miRNA and mRNA expression profiles sampled over multiple time-points during and after epileptogenesis in rats, and applied bi-clustering and Bayesian modelling to construct temporal miRNA-mRNA-mRNA interaction networks. Network analysis and enrichment of network inference with sequence- and human disease-specific information identified key regulatory miRNAs with the strongest influence on the mRNA landscape, and miRNA-mRNA interactions closely associated with epileptogenesis and subsequent epilepsy. Our findings underscore the complexity of miRNA-mRNA regulation, can be used to prioritise miRNA targets in specific systems, and offer insights into key regulatory processes in epileptogenesis with therapeutic potential for further investigation.
Keywords: Bayesian modelling; Epilepsy; Epileptogensis; Temporal expression profiling; miRNA-mRNA interactions; microRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA expression and gene regulation drive breast cancer progression and metastasis in PyMT mice.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 22;18(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0735-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27449149 Free PMC article.
-
Computational identification of hepatitis C virus associated microRNA-mRNA regulatory modules in human livers.BMC Genomics. 2009 Aug 11;10:373. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-373. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19671175 Free PMC article.
-
Epilepsy and microRNA.Neuroscience. 2013 May 15;238:218-29. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.02.027. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23485811 Review.
-
Modeling microRNA-mRNA interactions using PLS regression in human colon cancer.BMC Med Genomics. 2011 May 19;4:44. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-44. BMC Med Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21595958 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA and Epilepsy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:41-70. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26663178 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of sulforaphane in Alzheimer's disease: insights from an in-silico study.In Silico Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 1;12(2):96. doi: 10.1007/s40203-024-00267-4. eCollection 2024. In Silico Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39493676 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of a miRNA-mRNA network shared between acute pancreatitis and Epstein-Barr virus infection by integrated bioinformatics analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 15;19(11):e0311130. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311130. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39546499 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

