The effect of classroom size and ceiling height on college students' learning performance using virtual reality technology
- PMID: 38961227
- PMCID: PMC11222537
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-65754-2
The effect of classroom size and ceiling height on college students' learning performance using virtual reality technology
Abstract
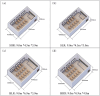
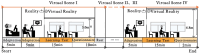
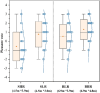
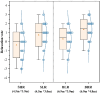
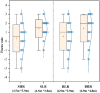
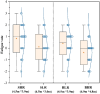
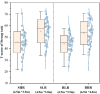
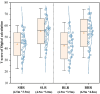
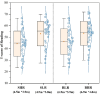
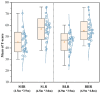
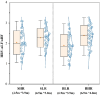
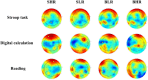
The physical characteristics of classrooms can significantly impact the physical and mental health as well as the learning performance of college students. This study investigates the effects of classroom size and ceiling height on learning performance using virtual reality technology. Four classroom settings were created: two small classrooms (40.5 m2) with ceiling heights of 3.0 m and 3.9 m, and two large classrooms (62.1 m2) with ceiling heights of 3.9 m and 4.8 m. 34 students participated in task tests while their subjective evaluations and physiological data were recorded. Results showed higher subjective ratings in larger classrooms with the same ceiling height. Classroom size did not significantly affect task test scores. However, there is a significant difference in Task test scores for ceilings of different heights with the same size classroom. The task test improved by 17.3% in the Big and High Room (BHR) and by 20.1% in the Small and Low Room (SLR). Physiological data revealed significant effects of ceiling height, with HRV-nLF/nHF and EEG-β power increasing by 26.5% and 53.9% in BHR, and by 10.7% and 22.8% in SLR, respectively. This study concludes that classroom size and ceiling height plays a crucial role in learning performance and provides insights for classroom design. It also establishes a framework for future research on the interplay between heart rate variability, EEG, and learning performance.
Keywords: Ceiling hight; EEG; HRV; Learning performance; Room size; VR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
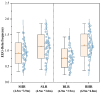
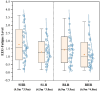
References
-
- Ge L, Gao Y, Meng X. Employing the spray system to alleviate the thermal action of air-conditioning in summer. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024;55:104133. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2024.104133. - DOI
-
- Liu S, Wang J, Meng L, Hu C, Meng X. Location of the phase-change material layer on thermal performance of light-weight walls. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2024;19:127–134. doi: 10.1093/ijlct/ctac096. - DOI
-
- Wu S, Qiu J. “Reading”, “listening” and sound, light environment. City Built Environ. 2024;2:1–16. doi: 10.1007/s44213-023-00022-z. - DOI
-
- Khan J, Hussain T, Javed MT, Meraj S. Effect of indoor environmental quality on human comfort and performance: A review. Ergon. Improv. Prod.: Proc. HWWE. 2022;2017(2):335–345.
-
- Song Y, Mao F, Liu Q. Human comfort in indoor environment: A review on assessment criteria, data collection and data analysis methods. IEEE Access. 2019;16:45–57.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

