Effect of chloride ions on persulfate/UV-C advanced oxidation of an alcohol ethoxylate (Brij 30)
- PMID: 38961237
- PMCID: PMC11222532
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66442-x
Effect of chloride ions on persulfate/UV-C advanced oxidation of an alcohol ethoxylate (Brij 30)
Abstract
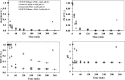
In the present study, the effect of chloride ions on the oxidative degradation of an alcohol ethoxylate (Brij 30) by persulfate (PS)/UV-C was experimentally explored using Brij 30 aqueous solution (BAS) and a domestic wastewater treatment plant effluent spiked with Brij 30. Brij 30 degradation occurred rapidly during the early stages of oxidation without affecting the water/wastewater matrix. Mineralization of intermediates of Brij 30 degradation markedly influenced by presence of chloride ions. Chloride ions at concentrations up to 50 mg/L accelerated the mineralization through reactions involving reactive chlorine species, which reduced the sink of SO4·- by Cl- scavenging at both initial pH of 6.0 and 3.0 in the case of BAS. The fastest mineralization was achieved under acidic conditions. The WWTP effluent matrix significantly influenced mineralization efficacy of the intermediates. Co-existence of and Cl- anions accelerated the mineralization of degradation products. Organic matter originating from the WWTP effluent itself had an adverse effect on the mineralization rate. The positive effects of organic and inorganic components present in the WWTP effluent were ranked in the following order of increasing influence: (Organic matter originating from the effluent + Cl- + ) < (Cl-) < (Cl- + ).
Keywords: Alcohol ethoxylate; Bicarbonate ions; Brij 30; Chloride ions; Persulfate/UV-C oxidation; Water/wastewater matrix.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
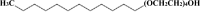


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

