A comparison of the TempO-Seq and Affymetrix microarray platform using RTqPCR validation
- PMID: 38961363
- PMCID: PMC11223392
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10586-7
A comparison of the TempO-Seq and Affymetrix microarray platform using RTqPCR validation
Abstract
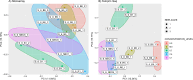
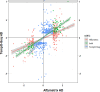
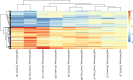
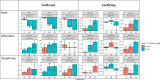
Next-generation risk assessment relies on mechanistic data from new approach methods, including transcriptome data. Various technologies, such as high-throughput targeted sequencing methods and microarray technologies based on hybridization with complementary probes, are used to determine differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The integration of data from different technologies requires a good understanding of the differences arising from the use of various technologies.To better understand the differences between the TempO-Seq platform and Affymetrix chip technology, whole-genome data for the volatile compound dimethylamine were compared. Selected DEGs were also confirmed using RTqPCR validation. Although the overlap of DEGs between TempO-Seq and Affymetrix was no higher than 37%, a comparison of the gene regulation in terms of log2fold changes revealed a very high concordance. RTqPCR confirmed the majority of DEGs from either platform in the examined dataset. Only a few conflicts were found (11%), while 22% were not confirmed, and 3% were not detected.Despite the observed differences between the two platforms, both can be validated using RTqPCR. Here we highlight some of the differences between the two platforms and discuss their applications in toxicology.
Keywords: Affymetrix; Chemical perturbation; Microarray; RT2 profiling arrays; RTqPCR; TempOSeq; Transcriptomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Parallel comparison of Illumina RNA-Seq and Affymetrix microarray platforms on transcriptomic profiles generated from 5-aza-deoxy-cytidine treated HT-29 colon cancer cells and simulated datasets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14 Suppl 9(Suppl 9):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S9-S1. Epub 2013 Jun 28. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23902433 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating gene expression in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mouse striatum using RNA-Seq and microarrays.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 24;6(3):e17820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017820. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21455293 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing next-generation sequencing and microarray technologies in a toxicological study of the effects of aristolochic acid on rat kidneys.Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Sep 19;24(9):1486-93. doi: 10.1021/tx200103b. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21834575
-
A semi-parametric statistical model for integrating gene expression profiles across different platforms.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Jan 11;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0847-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 26818110 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq technology and its application in fish transcriptomics.OMICS. 2014 Feb;18(2):98-110. doi: 10.1089/omi.2013.0110. Epub 2013 Dec 31. OMICS. 2014. PMID: 24380445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Toxicology in the 21st Century [Internet] Maryland (USA). National Institutes of Health; [ https://tox21.gov/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

