The coagulation status in women of endometriosis with stage IV
- PMID: 38961373
- PMCID: PMC11223421
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-024-03227-4
The coagulation status in women of endometriosis with stage IV
Abstract
Background: Endometriosis is considered as a systemic disease with the presence of proinflammatory cytokines in the circulation, which drives hypercoagulable state of endometriosis. Currently, endometriosis is classified into four stages: I (minimal), II (mild), III (moderate) and IV (severe). The aim of this study is to investigate the correlations between inflammatory markers and coagulation factors in patients diagnosed of endometriosis with stage IV.
Methods: This retrospective case-control study included 171 endometriosis patients with stage IV and 184 controls. Continuous data were expressed by mean ± standard deviation. Mann-Whitney U and χ2 tests were used to compare the medians and frequencies among the groups. Spearman analysis was conducted to determine the correlation among the measured parameters. The diagnostic values of the parameters differentiating endometriomas were tested by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
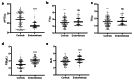
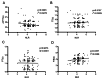
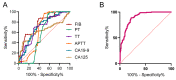
Results: The time of activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) was decreased and the concentration of fibrinogen (FIB) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were increased in women of endometriosis with stage IV. The APTT were negatively correlated with NLR while the concentrations of FIB were positively correlated with NLR. The ROC analysis showed that the Area under the curve (AUC) of FIB was 0.766 (95% confidence interval:0.717-0.814) with sensitivity and specificity reaching 86.5 and 60.9%, respectively. The AUC of CA125 and CA199 was 0.638 (95% confidence interval: 0.578-0.697), 0.71 (95% confidence interval: 0.656-0.763) with sensitivity and specificity reaching 40.9 and 91.8%, 80.7 and 56.5% respectively. The combination of these factors showed the highest AUC of 0.895 (0.862-0.927) with sensitivity of 88.9% and specificity of 77.7%.
Conclusion: In the present study, we found that inflammatory factors showed significant correlation with APTT or FIB in endometriosis with stage IV. Moreover, the coagulation factors combined with CA125 and CA199 were more reliable for identifying the endometriosis with stage IV.
Keywords: Endometriosis; Hypercoagulability; Inflammation; Stage IV.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is there a correlation between inflammatory markers and coagulation parameters in women with advanced ovarian endometriosis?BMC Womens Health. 2019 Dec 30;19(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12905-019-0860-9. BMC Womens Health. 2019. PMID: 31888633 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the combination of serum CA-125 for stages III and IV endometriosis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(11):2011-4. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013. PMID: 23769549
-
Noninvasive evaluation of ovarian endometriosis: a single-center experience.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Apr;10(4):4728-4735. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-481. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33966422
-
Diagnostic value of serum D-dimer, CA125, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in differentiating ovarian cancer and endometriosis.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2019 Nov;147(2):212-218. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.12949. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2019. PMID: 31469423
-
Coagulation Status in Women With Endometriosis.Reprod Sci. 2018 Apr;25(4):559-565. doi: 10.1177/1933719117718273. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Reprod Sci. 2018. PMID: 28681683
Cited by
-
Assessment of the prognostic value of CA125 for miscarriage risk in patients with threatened abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 24;20(6):e0326384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326384. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40554540 Free PMC article.
-
Complement and coagulation cascade cross-talk in endometriosis and the potential of Janus Kinase inhibitors-a network meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 8;16:1619434. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1619434. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40698088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis. 1996. Fertil Steril. 1997;67(5):817–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

