Minimum four-year clinical outcomes after on-table reconstruction technique for Dubberley type III in coronal shear fractures of the capitellum and trochlea: a report of 10 patients
- PMID: 38961389
- PMCID: PMC11221089
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-024-07628-2
Minimum four-year clinical outcomes after on-table reconstruction technique for Dubberley type III in coronal shear fractures of the capitellum and trochlea: a report of 10 patients
Abstract
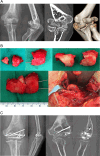
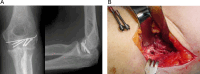
Purpose: Comminuted coronal shear fractures of the distal humerus represent rare injuries and are difficult to treat, especially comminuted capitellum and trochlear fractures (Dubberley Type III). The on-table reconstruction technique of comminuted articular fractures may be an option, although it has not been reported in the coronal shear fracture of the distal humerus. The aim of the present case series is to determine the functional and radiological outcomes of on-table reconstructed Dubberley III fractures.
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted of 10 patients with Dubberley type III fractures in coronal shear fractures of the capitellum and trochlea who underwent an 'on-table' reconstruction technique between January 2009 and October 2019. All patients were evaluated using the disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) score, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons(ASES) score, Mayo Elbow Score Performance Index (MEPI) score and at least 4 years later.
Results: All cases achieved union. At the final follow-up, the mean range of elbow motion was 11.5°of flexion contracture and 131.9° of further flexion. The mean DASH score was 21.2 (5.7) points (range 13.3-32.5). The mean ASES score was 88.6 ± 7.4 (range, 77 to 100). The mean MEPI score was 87 (10) points (range 70-100). In complication, partial osteonecrosis of capitellum is developed in one patient. One patient had heterotopic ossification without functional impairment.
Conclusion: The on-table reconstruction technique can be a reliable option in the surgical treatment of complex distal humerus fractures. This technique allows anatomical reduction of comminuted capitellum and trochlea, with a low risk of avascular necrosis over 4 years of follow-up.
Level of evidence: Level IV, retrospective case series.
Keywords: Capitellum; Coronal shear fracture; On-table reconstruction; Trochlea.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Open reduction and internal fixation of coronal fractures of the capitellum in patients older than 65 years.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016 Mar;25(3):369-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.12.004. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016. PMID: 26927432
-
Outcome determinants for coronal shear fractures of the distal humerus.Int Orthop. 2024 May;48(5):1295-1302. doi: 10.1007/s00264-024-06151-2. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Int Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38502337
-
Treatment of capitellar and trochlear fractures with posterior comminution: minimum 2-year follow-up.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019 May;28(5):931-938. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Dec 28. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019. PMID: 30595502
-
Involvement of the medial and lateral epicondyles in distal humeral coronal shear fractures: Case series and literature review.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022 Oct;32(7):1341-1356. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-03113-x. Epub 2021 Sep 12. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34514547 Review.
-
The impact of associated injuries and fracture classifications on the treatment of capitellum and trochlea fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2018 Jun;54(Pt A):37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.04.028. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29684669
References
-
- Mancini GB, Fiacca C, Picuti G. Resection of the radial capitellum. Long-term results. Ital J Orthop Traumatol. 1989;15(3):295–302. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

