Knowledge of Alzheimer's disease and associated factors among adults in Zhuhai, China: a cross-sectional analysis
- PMID: 38961390
- PMCID: PMC11220978
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-19289-w
Knowledge of Alzheimer's disease and associated factors among adults in Zhuhai, China: a cross-sectional analysis
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess the public knowledge regarding Alzheimer's Disease (AD) in Zhuhai, China, focusing on identifying knowledge gaps and the influence of demographic and health factors.
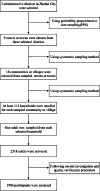
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in Zhuhai, China, from October to November 2022. A total of 1986 residents from 18 communities were selected employing stratified multi-stage equi-proportional sampling. Questionnaires covering general information and the Alzheimer's Disease Knowledge Scale (ADKS) were investigated face-to-face. Ordinal multiclass logistic regression was applied to assess the relationship between AD awareness and demographic and health characteristics.
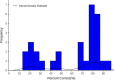
Results: The average ADKS score was 18.5 (SD = 3.36) in Zhuhai. The lowest awareness rates were observed in the "Symptoms" and "Caregiving" subdomains of ADKS, with rates of 51.01% and 43.78%, respectively. The correct rates for the 30 ADKS questions ranged from 16.62 to 92.6%, showing a bimodal pattern with clusters around 80% and 20%. Women (OR = 1.203, 95% CI: 1.009-1.435), individuals aged 60 years or older (OR = 2.073, 95% CI: 1.467-2.932), those living in urban areas (OR = 1.361, 95% CI: 1.117-1.662), higher average monthly household income per capita (OR = 1.641, 95% CI: 1.297-2.082), and without any neurological or mental disorders (OR = 1.810, 95% CI: 1.323-2.478) were more likely to have higher levels of awareness about Alzheimer's disease.
Conclusions: Adults in Zhuhai show a limited knowledge of AD, particularly in the 'Symptoms' and 'Caregiving' subdomains. Upcoming health campaigns must focus on bridging the knowledge gaps in different subdomains of AD, especially among subgroups with lower awareness, as identified in our study.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Cross-sectional study; Knowledge; Public.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A study of knowledge on Alzheimer's disease and attitudes of Chinese social residents toward Alzheimer's disease: A cross-sectional survey in China.Public Health Nurs. 2024 Sep-Oct;41(5):943-950. doi: 10.1111/phn.13354. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Public Health Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38946470
-
Assessing Alzheimer's disease knowledge among Egyptian medical students in the context of recent educational reforms.BMC Med Educ. 2025 May 5;25(1):654. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07258-9. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40325427 Free PMC article.
-
Public knowledge about Alzheimer's disease in Egypt: a cross-sectional survey.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025 May 26;37(1):163. doi: 10.1007/s40520-025-02967-z. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025. PMID: 40415129 Free PMC article.
-
Testing the knowledge of Alzheimer's disease via an intervention study among community health service center staff in Jiaxing, China.Front Public Health. 2023 Jan 27;10:969653. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.969653. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36777777 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Knowledge and perceptions of Alzheimer's disease in three ethnic groups of younger adults in the United Kingdom.BMC Public Health. 2021 Jun 12;21(1):1124. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11231-8. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34118921 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Knowledge and attitudes towards Alzheimer's disease among adult residents in Jiulongpo, Chongqing, China: A cross-sectional survey.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 30;20(6):e0327346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327346. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40587504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Sappagh S, Saleh H, Ali F, Amer E, Abuhmed T. Two-stage deep learning model for Alzheimer’s disease detection and prediction of the mild cognitive impairment time. Neural Comput Applic. 2022;34:14487–509. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07263-9. - DOI
-
- Nichols E, Steinmetz JD, Vollset SE, Fukutaki K, Chalek J, Abd-Allah F, et al. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health. 2022;7:e105–25. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00249-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- ADI - Dementia statistics n.d. https://www.alzint.org/about/dementia-facts-figures/dementia-statistics/ (accessed November 22, 2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical