The role of cytoreductive nephrectomy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma in immune-oncology era (SEVURO-CN): study protocol for a multi-center, prospective, randomized trial
- PMID: 38961439
- PMCID: PMC11223430
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-024-08234-2
The role of cytoreductive nephrectomy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma in immune-oncology era (SEVURO-CN): study protocol for a multi-center, prospective, randomized trial
Abstract
Background: The role of cytoreductive nephrectomy (CN) in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) remains unclear in the immuno-oncology (IO) era. The results of two randomized trials, CARMENA and SURTIME, questioned the role and timing of CN. However, despite the latest advances in the systemic treatment of mRCC, previous trials have only used targeted therapy, and no studies have fully investigated the role of CN in immune checkpoint inhibitor (CPI) settings, and there is an urgent need for future studies to better define the role and timing of CN.
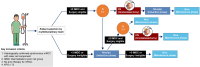
Methods: This study is an open-label, multi-center, parallel, prospective, randomized, interventional clinical study to evaluate the efficacy of CN in combination with CPIs in mRCC patients with International mRCC Database Consortium (IMDC) intermediate- and poor-risk. Synchronous mRCC patients with ≤ 3 IMDC risk features will be randomly allocated to three groups (1, upfront CN; 2, deferred CN; and 3, systemic therapy [ST] only). For ST, the nivolumab plus ipilimumab combination regimen, one of the standard regimens for intermediate- and poor-risk mRCC, is chosen. The primary endpoint is overall survival. The secondary endpoints are progression-free survival, objective response rate, number of participants with treatment-related adverse events, and number of participants with surgical morbidity. We will analyze the genetic mutation profiles of the tumor tissue, circulating tumor DNA, urine tumor DNA, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. The gut and urine microbial communities will be analyzed. The study will begin in 2022 and will enroll 55 patients.
Discussion: This study is one of the few prospective randomized trials to evaluate the benefit of CN in the treatment of synchronous mRCC in the IO era. The SEVURO-CN trial will help identify the role and timing of CN, thereby rediscovering the value of CN.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT05753839. Registered on 3 March 2023.
Keywords: Cytoreductive nephrectomy; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Ipilimumab; Kidney neoplasms; Nivolumab; Prospective studies; Renal cell carcinoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Warren MA, Golshayan AR, Sahi C, et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5794–5799. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.4809. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mekhail TM, Abou-Jawde RM, Boumerhi G, Malhi S, Wood L, Elson P, et al. Validation and extension of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering prognostic factors model for survival in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:832–841. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.179. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical