Screening primary carnitine deficiency in 10 million Chinese newborns: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38961493
- PMCID: PMC11220949
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-024-03267-x
Screening primary carnitine deficiency in 10 million Chinese newborns: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Primary carnitine deficiency (PCD) is a rare autosomal recessive fatty acid oxidation disorder caused by variants in SLC22A5, with its prevalence and SLC22A5 gene mutation spectrum varying across races and regions. This study aimed to systematically analyze the incidence of PCD in China and delineate regional differences in the prevalence of PCD and SLC22A5 gene variants.
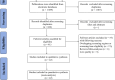
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Chinese databases were searched up to November 2023. Following quality assessment and data extraction, a meta-analysis was performed on screening results for PCD among Chinese newborns.
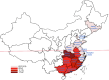
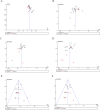
Results: After reviewing 1,889 articles, 22 studies involving 9,958,380 newborns and 476 PCD cases were included. Of the 476 patients with PCD, 469 underwent genetic diagnosis, revealing 890 variants of 934 alleles of SLC22A5, among which 107 different variants were detected. The meta-analysis showed that the prevalence of PCD in China was 0.05‰ [95%CI, (0.04‰, 0.06‰)] or 1/20 000 [95%CI, (1/16 667, 1/25 000)]. Subgroup analyses revealed a higher incidence in southern China [0.07‰, 95%CI, (0.05‰, 0.08‰)] than in northern China [0.02‰, 95%CI, (0.02‰, 0.03‰)] (P < 0.001). Furthermore, the result of the meta-analysis showed that the frequency of the variant with c.1400C > G, c.51C > G, c.760C > T, c.338G > A, and c.428C > T were 45% [95%CI, (34%, 59%)], 26% [95%CI, (22%, 31%)], 14% [95%CI, (10%, 20%)], 6% [95%CI, (4%, 8%)], and 5% [95%CI, (4%, 8%)], respectively. Among the subgroup analyses, the variant frequency of c.1400C > G in southern China [39%, 95%CI, (29%, 53%)] was significantly lower than that in northern China [79‰, 95%CI, (47‰, 135‰)] (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: This study systematically analyzed PCD prevalence and identified common SLC22A5 gene variants in the Chinese population. The findings provide valuable epidemiological insights and guidance for future PCD screening effects in newborns.
Keywords: SLC22A5; Incidence; Meta-analysis; Neonatal screening; Primary carnitine deficiency; Variant.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The global prevalence and genetic spectrum of primary carnitine deficiency.BMC Genom Data. 2025 Jul 7;26(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12863-025-01336-z. BMC Genom Data. 2025. PMID: 40624458 Free PMC article.
-
Newborn screening of primary carnitine deficiency: clinical and molecular genetic characteristics.Ital J Pediatr. 2025 Mar 11;51(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13052-025-01911-1. Ital J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40069787 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and genetic characteristics of patients with primary carnitine deficiency identified through newborn screening.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021 Dec 4;16(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-02126-3. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. PMID: 34863234 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors influencing fear of disease progression in stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis with a focus on China.BMJ Open. 2025 Jun 6;15(6):e091605. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-091605. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40480663 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational weight gain below instead of within the guidelines per class of maternal obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of obstetrical and neonatal outcomes.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022 Sep;4(5):100682. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2022.100682. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022. PMID: 35728780
Cited by
-
Assessment and Application of Acylcarnitines Summations as Auxiliary Quantization Indicator for Primary Carnitine Deficiency.Int J Neonatal Screen. 2025 Jun 19;11(2):47. doi: 10.3390/ijns11020047. Int J Neonatal Screen. 2025. PMID: 40559184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guerrero Cervera B, Donoso Trenado V, Fernández-Sellers C, Vila Clérigues N, Correcher Medina P, Zorio E. Cardiomyopathy associated with primary carnitine deficiency in adults: lack of complete response in patients with delayed treatment initiation. Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition) 2024;77:265–267. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2023.08.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 2021ZD01002/the Key Project on Science and Technology Program of the Fujian Health Commission
- 2020J01327/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
- 2020GGB017/Fujian Provincial Health Technology Project
- 2022CXA033/Fujian Provincial Health Technology Project
- 2020Y9143/Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

