Insights of early feeding regime supplemented with glutamine and various levels of omega-3 in broiler chickens: growth performance, muscle building, antioxidant capacity, intestinal barriers health and defense against mixed Eimeria spp infection
- PMID: 38961536
- PMCID: PMC11225632
- DOI: 10.1080/01652176.2024.2373287
Insights of early feeding regime supplemented with glutamine and various levels of omega-3 in broiler chickens: growth performance, muscle building, antioxidant capacity, intestinal barriers health and defense against mixed Eimeria spp infection
Abstract
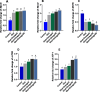
Early nutritional management approach greatly impacts broilers' performance and resistance against coccidiosis. The current study explored the impact of post-hatch feeding with a combination of glutamine (Glut) and different levels of omega-3 on broiler chickens' growth performance, muscle building, intestinal barrier, antioxidant ability and protection against avian coccidiosis. A total of six hundred Cobb 500 was divided into six groups: first group (fed basal diet and unchallenged (control) and challenged (negative control, NC) groups were fed a basal diet without additives, and the other groups were infected with Eimeria spp and supplemented with 1.5% Glut alone or with three different levels of omega-3 (0.25, 0.5 and 1%) during the starter period. Notable improvement in body weight gain was observed in the group which fed basal diet supplemented with glut and 1% omega 3 even after coccidia infection (increased by 25% compared challenged group) while feed conversion ratio was restored to control. Myogeneis was enhanced in the group supplemented with Glut and omega-3 (upregulation of myogenin, MyoD, mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase and insulin like growth factor-1 and downregulating of myostatin genes). Groups supplemented with Glut and higher levels of omega-3 highly expressed occluding, mucin-2, junctional Adhesion Molecule 2, b-defensin-1 and cathelicidins-2 genes. Group fed 1% Glut + omega-3 showed an increased total antioxidant capacity and glutathione peroxidase and super oxide dismutase enzymes activities with reduced levels of malondialdehyde, reactive oxygen species and H2O2. Post-infection, dietary Glut and 1% omega-3 increased intestinal interleukin-10 (IL) and secretory immunoglobulin-A and serum lysozyme, while decreased the elevated inflammatory mediators comprising interleukin IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, nitric oxide (NO) and inducible NO synthase. Fecal oocyst excretion and lesions score severity were lowered in the group fed 1% Glut and omega 3. Based on these findings, dietary Glut and omega-3 supplementation augmented restored overall broilers' performance after coccidial challenge.
Keywords: Post hatch feeding; coccidiosis; glutamine; omega-3; tight junction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abbas R, Iqbal Z, Mansoor M, Sindhu Z, Zia M, Khan J.. 2013. Role of natural antioxidants for the control of coccidiosis in poultry. Pak Vet J. 33:401–407.
-
- Abdel-Raheem SM,Mohammed ESY,Mahmoud RE,El Gamal MF,Nada HS,El-Ghareeb WR,Marzok M,Meligy AMA,Abdulmohsen M,Ismail H, et al. .. 2023. Double-Fermented Soybean Meal Totally Replaces Soybean Meal in Broiler Rations with Favorable Impact on Performance, Digestibility, Amino Acids Transporters and Meat Nutritional Value. Animals. 13(6):1030. doi: 10.3390/ani13061030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdulkarimi R, Shahir MH, Daneshyar M.. 2019. Effects of dietary glutamine and arginine supplementation on performance, intestinal morphology and ascites mortality in broiler chickens reared under cold environment. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 32(1):110–117. doi: 10.5713/ajas.17.0150. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdulla NR, Loh TC, Akit H, Sazili AQ, Foo HL, Kareem KY, Mohamad R, Abdul Rahim R.. 2017. Effects of dietary oil sources, calcium and phosphorus levels on growth performance, carcass characteristics and bone quality of broiler chickens. J Appl Anim Res. 45(1):423–429. doi: 10.1080/09712119.2016.1206903. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
