The prognostic value of right ventricular outflow tract velocity time integral in patients with pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 38961603
- PMCID: PMC11424340
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.14934
The prognostic value of right ventricular outflow tract velocity time integral in patients with pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
Aims: Right ventricular (RV) failure is one of the leading causes of death in patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH). Conventional echocardiographic parameters are not included in risk stratification and follow-up for prognostic assessment due to PH's diverse nature and the RV's complex geometry. RV outflow tract velocity time integral (RVOT VTI) is a simple, non-invasive estimate of pulmonary flow and an echocardiographic surrogate of RV stroke volume. In this study, we aimed to define the prognostic value of RVOT VTI in PH patients.
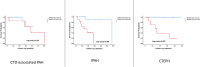
Methods: Sixty-three subjects with idiopathic PAH (IPAH) (n = 23), connective tissue disease-associated PAH (CTD-associated PAH) (n = 19) and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) (n = 21) were retrospectively included. A comprehensive two-dimensional echocardiographic evaluation, including RVOT-VTI measurement, was performed during the follow-up and the New York Heart Association functional class (NYHA FC), 6 min walk distance (6MWD) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels were recorded.
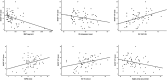
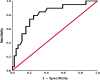
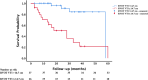
Results: The median age of the whole cohort was 63 years (52-68), and 47 (74.6%) of the patients were women. The median follow-up period was 20 months (11-33), and 20 (31.7%) patients died in this period. BNP values were higher [317 (210-641) vs 161 (47-466), P = 0.02], and 6MWD values were lower [197.5 ± 89.5 vs 339 ± 146.3, P < 0.0001] in the non-survivor group, and the non-survivor group had a worse NYHA-FC (P = 0.02). Among echocardiographic data, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) (15.4 ± 4.8 vs 18.6 ± 4.2, P = 0.01) and RVOT VTI (11.9 ± 4.1 vs 17.2 ± 4.3, P < 0.0001) values were lower whereas right atrial area (RAA) (26.9 ± 10.1 vs 22.2 ± 7.1, P = 0.04) values were higher in the non-survivor group. The area under curve of the RVOT VTI for predicting mortality was 0.82 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.715-0.940, P < 0.0001], and the best cut-off value was 14.7 cm with a sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 77%. Survival was significantly lower in subjects with RVOT VTI ≤ 14.7 cm (log-rank P < 0.0001). Survival rates for patients with RVOT VTI ≤ 14.7 cm were 70% at 1 year, 50% at 2 years, %29 at 3 years and 21% at 5 years. The univariate determinants of all-cause mortality were BNP [hazard ratio (HR) 1.001 (1.001-1.002), P = 0.001], 6MWD [HR 0.994 (0.990-0.999), P = 0.012] and NYHA-FC III-IV [HR 3.335 (1.103-10.083), P = 0.03], TAPSE [HR 0.838 (0.775-0.929), P = 0.001], RAA [HR 1.072 (1.013-1.135), P = 0.016] and RVOT VTI [HR 0.819 (0.740-0.906), P < 0.0001]. RVOT VTI was found to be the only independent determinant of mortality [HR 0.857 (0.766-0.960), P = 0.008].
Conclusions: The decreased RVOT VTI predicts mortality in patients with PH and each 1 mm decrease in RVOT VTI increases the risk of mortality by 14.3%. This parameter might serve as an additional parameter in the follow-up of these patients especially when 6MWD and NYHA-FC could not be determined.
Keywords: Mortality; Pulmonary hypertension; Right heart failure; Right ventricular outflow tract velocity time integral.
© 2024 The Author(s). ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The right ventricular outflow tract in pediatric pulmonary hypertension-Data from the European Pediatric Pulmonary Vascular Disease Network.Echocardiography. 2018 Jun;35(6):841-848. doi: 10.1111/echo.13852. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Echocardiography. 2018. PMID: 29505663
-
The Usefulness of the TAPSE/sPAP Ratio for Predicting Survival in Medically Treated Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension.Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2023 Oct;51(7):470-477. doi: 10.5543/tkda.2023.78074. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2023. PMID: 37861261 English.
-
Echocardiographic Assessment of Right Ventricular Function and Response to Therapy in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Am J Cardiol. 2019 Oct 15;124(8):1298-1304. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.07.026. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31481176
-
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Screening, Management, and Treatment [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2013 Apr. Report No.: 13-EHC087-EF. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2013 Apr. Report No.: 13-EHC087-EF. PMID: 23741759 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Prognostic value of right ventricular free-wall longitudinal strain in aortic stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cardiol. 2024 Aug;84(2):80-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2023.11.008. Epub 2023 Dec 2. J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38043709
Cited by
-
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Use in Hemodynamic Assessment.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 10;13(6):1426. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061426. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564145 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benza RL, Miller DP, Gomberg‐Maitland M, Frantz RP, Foreman AJ, Coffey CS, et al. Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: insights from the registry to evaluate early and long‐term pulmonary arterial hypertension disease management (REVEAL). Circulation 2010;122:164‐172. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.898122 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

