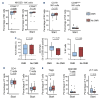
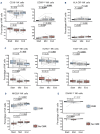
Response to DA-EPOCH-R is associated with activation of 'fitter' cytotoxic T cells in patients with newly diagnosed double and triple hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 38961740
- PMCID: PMC11532709
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285170
Response to DA-EPOCH-R is associated with activation of 'fitter' cytotoxic T cells in patients with newly diagnosed double and triple hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic analysis of CD5 expression in double-hit diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and effectiveness comparison in patients treated with dose-adjusted EPOCH plus rituximab/R-CHOP regimens.Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2019 Aug 19;9:33-43. doi: 10.2147/BLCTT.S216292. eCollection 2019. Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31692510 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-center analysis of the impact of DA-EPOCH-R dose-adjustment on clinical outcomes of patients with double/triple-hit lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2023 Jan;64(1):107-118. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2022.2140281. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Leuk Lymphoma. 2023. PMID: 36323309
-
Efficacy of dose-adjusted EPOCH plus rituximab/R-CHOP regimens and the prognosis analysis in patients with MYC, BCL2/BCL6 gene copy number gain lymphoma and double-hit lymphoma: results from a single institution retrospective clinical study.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Feb 11;11:1363-1372. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S192143. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 30809101 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on chemotherapy for the management of double-hit lymphoma.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Apr;21(6):653-661. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1727445. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32066288 Review.
-
Drug therapy for double-hit lymphoma.Drugs Context. 2019 Dec 2;8:2019-8-1. doi: 10.7573/dic.2019-8-1. eCollection 2019. Drugs Context. 2019. PMID: 31844420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, et al. . CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):235-242. - PubMed
-
- Dunleavy K, Fanale MA, Abramson JS, et al. . Dose-adjusted EPOCH-R (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab) in untreated aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with MYC rearrangement: a prospective, multicentre, single-arm phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2018;5(12):e609-e617. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Howlett C, Snedecor SJ, Landsburg DJ, et al. . Front-line, dose-escalated immunochemotherapy is associated with a significant progression-free survival advantage in patients with double-hit lymphomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Haematol. 2015;170(4):504-514. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

