Perivascular spaces, plasma GFAP, and speeded executive function in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 38961774
- PMCID: PMC11350014
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14081
Perivascular spaces, plasma GFAP, and speeded executive function in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
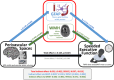
Introduction: We investigated the effect of perivascular spaces (PVS) volume on speeded executive function (sEF), as mediated by white matter hyperintensities (WMH) volume and plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in neurodegenerative diseases.
Methods: A mediation analysis was performed to assess the relationship between neuroimaging markers and plasma biomarkers on sEF in 333 participants clinically diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease/mild cognitive impairment, frontotemporal dementia, or cerebrovascular disease from the Ontario Neurodegenerative Disease Research Initiative.
Results: PVS was significantly associated with sEF (c = -0.125 ± 0.054, 95% bootstrap confidence interval [CI] [-0.2309, -0.0189], p = 0.021). This effect was mediated by both GFAP and WMH.
Discussion: In this unique clinical cohort of neurodegenerative diseases, we demonstrated that the effect of PVS on sEF was mediated by the presence of elevated plasma GFAP and white matter disease. These findings highlight the potential utility of imaging and plasma biomarkers in the current landscape of therapeutics targeting dementia.
Highlights: Perivascular spaces (PVS) and white matter hyperintensities (WMH) are imaging markers of small vessel disease. Plasma glial fibrillary protein acidic protein (GFAP) is a biomarker of astroglial injury. PVS, WMH, and GFAP are relevant in executive dysfunction from neurodegeneration. PVS's effect on executive function was mediated by GFAP and white matter disease.
Keywords: cerebrovascular diseases; executive function; neurodegenerative diseases; perivascular spaces; plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein; white matter hyperintensities.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
D.A. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. J.O. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. M.R. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. G.F. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. A.A.D. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. R.A.H. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. F.G. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. P.M.M. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. J.S.R. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. M.W.A. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. C.J.M.S. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. V.Y. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. C.B. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. M.O. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. W.S. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. J.Z. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. M.C.T. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. E.R. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. D.F.T.‐W. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. L.C. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. S.K. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. D.D. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. J.M. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. D.S. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. G.S. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. C.E.F. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. M.B. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. A.H. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. M.A.B. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. M.F. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. H.C. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. E.F. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. A.F. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. R.B. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. S.S. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. H.Z. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. R.H.S. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. M.M. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. S.E.B. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. J.R. reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. D.A. reports funding (travel and meetings) from Biogen, Roche, Teva, Novartis, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Genzyme, and Sanofi outside the submitted work. H.Z. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Alzecure, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, and Roche, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). C.E.F. receives grant funding from NIA, NIH, CCNA, CIHR, ADDF, TDRA, Mito2i, the Hilary and Galen Weston Foundation, and Novo Nordisk. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Alzheimer Society of London
- Middlesex Doctoral Graduate Research Scholarship
- Dr. Sandra Black Centre for Brain Resilience and Recovery
- Linda C. Campbell Foundation
- Weston UK Brain Institute,
- Foundation Leducq Transatlantic Network of Excellence for their support of PVS-related studies
- #2023-00356/Swedish Research Council
- #2022-01018/Swedish Research Council
- #2019-02397/Swedish Research Council
- 101053962/European Union's Horizon Europe research and innovation programme
- #ALFGBG-71320/Swedish State Support for Clinical Research
- #201809-2016862/Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF)
- AD Strategic Fund
- Bluefield Project, Cure Alzheimer's Fund
- Olav Thon Foundation
- Erling-Persson Family Foundation
- #FO2022-0270/Stiftelsen för Gamla Tjänarinnor, Hjärnfonden, Sweden
- European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- JPND2021-00694/European Union Joint Programme-Neurodegenerative Disease Research
- National Institute for Health and Care Research University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre
- UKDRI-1003/UK Dementia Research Institute at UCL
- Brain and Behavior Foundation
- National Institute on Ageing
- BrightFocus Foundation
- Canadian Institute of Health Research
- Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging
- Centre for Ageing and Brain Health Innovation
- Centre for Addiction and Mental Health
- #ADSF-21-831376-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- #ADSF-21-831381-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- #ADSF-21-831377-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

