CCL2 promotes EGFR-TKIs resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via the AKT-EMT pathway
- PMID: 38961814
- PMCID: PMC11532253
- DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2024106
CCL2 promotes EGFR-TKIs resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via the AKT-EMT pathway
Abstract
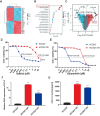
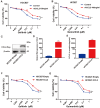
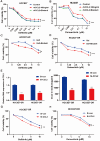
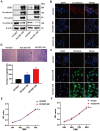
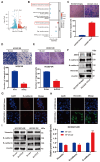
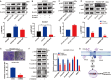
Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) represents a primary cause of treatment failure in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) is recently found to play a pivotal role in determining anti-cancer treatment response. However, the role and mechanism of CCL2 in the development of EGFR-TKIs resistance have not been fully elucidated. In the present study, we focus on the function of CCL2 in the development of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC cells. Our results show that CCL2 is aberrantly upregulated in EGFR-TKIs-resistant NSCLC cells and that CCL2 overexpression significantly diminishes sensitivity to EGFR-TKIs. Conversely, CCL2 suppression by CCL2 synthesis inhibitor, bindarit, or CCL2 knockdown can reverse this resistance. CCL2 upregulation can also lead to enhanced migration and increased expressions of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cells, which could also be rescued by CCL2 knockdown or inhibition. Furthermore, our findings suggest that CCL2-dependent EGFR-TKIs resistance involves the AKT-EMT signaling pathway; inhibition of this pathway effectively attenuates CCL2-induced cell migration and EMT marker expression. In summary, CCL2 promotes the development of acquired EGFR-TKIs resistance and EMT while activating AKT signaling in NSCLC. These insights suggest a promising avenue for the development of CCL2-targeted therapies that prevent EGFR-TKIs resistance in NSCLC.
Keywords: CCL2; EGFR-TKIs resistance; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. . 2021;71:209–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, Mariotto AB, Yabroff KR, Jemal A, Kramer J, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. . 2022;72:409–436. doi: 10.3322/caac.21731. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. . 2012;13:239–246. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

