Roles of estrogen and its receptors in polycystic ovary syndrome
- PMID: 38961865
- PMCID: PMC11219844
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1395331
Roles of estrogen and its receptors in polycystic ovary syndrome
Abstract
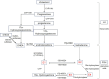
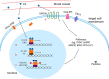
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disorder characterized by abnormal steroid hormone levels in peripheral blood and poor-quality oocytes. In the ovary, androgen is produced by theca cells, and estrogen is produced by granulosa cells. Androgen is converted to estrogen in granulosa cells, with cytochrome P450 aromatase as the limiting enzyme during this process. Estrogen receptors (ER) include ER alpha, ER beta, and membrane receptor GPR30. Studies have demonstrated that the abnormal functions of estrogen and its receptors and estradiol synthesis-related enzymes are closely related to PCOS. In recent years, some estrogen-related drugs have made significant progress in clinical application for subfertility with PCOS, such as letrozole and clomiphene. This article will elaborate on the recent advances in PCOS caused by abnormal expression of estrogen and its receptors and the application of related targeted small molecule drugs in clinical research and treatment.
Keywords: estrogen; estrogen receptor; estrogen signaling; ovary; polycystic ovary syndrome.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Zhang, Wang, Xue, Ying and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

