Peptide Conjugated Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Enhanced Tumor Targeting
- PMID: 38961887
- PMCID: PMC11217788
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.95251
Peptide Conjugated Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Enhanced Tumor Targeting
Abstract
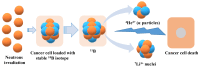
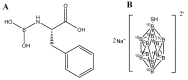
A cutting-edge non-invasive cancer treatment method called boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) allows for the removal of cancerous tumor cells with the least possible damage to healthy tissue. It involves the exposure of cancer cells with low-energy thermal neutrons, boron-10 (10B) cellular uptake causes cancer cell death by producing alpha particles and recoiling lithium-7 (7 Li) nuclei. Despite positive outcomes from clinical trials conducted all around the world, these substances have relatively limited tumor selectivity or low boron content per molecule. The development of new boron delivery agents with more selectivity and enhanced boron loading would advance this technique and promote its use in clinics as a primary cancer treatment. As peptide-binding cell surface receptors are typically overexpressed on cancer cells, they can be seen as interesting targets for targeted tumor therapy. The attachment of meta-carboranes to peptide conjugates that target tumor cells specifically by their overexpressed receptors may be a method to get around these problems. A state-of-the-art overview of current developments in the application of BNCT for cancer targeted therapy via peptide conjugation is the goal of this review.
Keywords: BNCT; Peptide conjugation; Tumor targeting; targeting peptides and BNCT designing.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: current status and future prospects.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jun 1;11(11):3987-4002. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0035. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15930333 Review.
-
The basis and advances in clinical application of boron neutron capture therapy.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Nov 7;16(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01939-7. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34743756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Boron neutron capture therapy: Moving toward targeted cancer therapy.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Apr-Jun;12(2):520-5. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.176167. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27461603 Review.
-
Boron neutron capture therapy of brain tumors: past history, current status, and future potential.Cancer Invest. 1996;14(6):534-50. doi: 10.3109/07357909609076899. Cancer Invest. 1996. PMID: 8951358 Review.
-
A realistic appraisal of boron neutron capture therapy as a cancer treatment modality.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018 Jun 19;38(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0280-5. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29914575 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances in Nanotheranostic Systems for Concurrent Cancer Imaging and Therapy: An Overview of the Last 5 Years.Molecules. 2024 Dec 19;29(24):5985. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245985. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Brain Drug Delivery with Macromolecules Through Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jan 15;17(1):109. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010109. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 39861756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hu K, Yang Z, Zhang L. et al. Boron agents for neutron capture therapy. Coord Chem Rev. 2020;405:213139.
-
- Purohit M, Kumar M. Boron neutron capture therapy: History and recent advances. Mater Today Proc. 2022.
-
- Mitusova K, Peltek OO, Karpov TE, Muslimov AR, Zyuzin M V, Timin AS. Overcoming the blood-brain barrier for the therapy of malignant brain tumor: current status and prospects of drug delivery approaches. J Nanobiotechnology 2022 201 [Internet] 2022. [cited 6 April 2023]; 20: 1-40. Available at: https://link.springer.com/articles/10.1186/s12951-022-01610-7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- He H, Li J, Jiang P, The basis and advances in clinical application of boron neutron capture therapy. Radiat Oncol [Internet] 2021. [cited 6 April 2023]; 16: 1-8. Available at: https://link.springer.com/articles/10.1186/s13014-021-01939-7. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

