Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability, and validity of the Persian version of the overactive bladder questionnaire (OAB-V8)
- PMID: 38961992
- PMCID: PMC11219307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32298
Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability, and validity of the Persian version of the overactive bladder questionnaire (OAB-V8)
Abstract
Background and objectives: Overactive bladder (OAB) is characterized by urinary frequency and is recognized as a disorder. Various tools are available for diagnosing this condition. This study aimed to evaluate the reliability and validity of the Persian version of the 8-item Overactive Bladder Scale (OAB-V8).
Methods: This analytical cross-sectional study was conducted on a sample of 150 OAB patients. The OAB-V8 scale was translated and culturally adapted following established guidelines. Face and content validity were assessed using the Impact Score (IS), Content Validity Index (CVI), and Content Validity Ratio (CVR) indices. Reliability was evaluated by calculating Cronbach's alpha (α) and utilizing the test-retest method (Intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC)). Construct validity was explored through exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). All statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS version 24 and AMOS version 24, with a significance level set at 5 %.
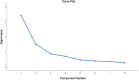
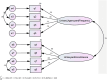
Results: The face validity was confirmed, with all items having an IS value greater than 1.5. Content validity was also confirmed, as most items had a Content Validity Index (CVI) higher than 0.79, and the average Content Validity Ratio (CVR) value was 0.96. In the initial phase of Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA), the sample adequacy and suitability of the exploratory analysis were confirmed (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) test value = 0.784, Bartlett's Test p-value <0.05). Two dimensions explaining 61.87 % of the variance were then extracted. In the Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA), the fit indices were deemed acceptable (χ^2/df = 2.006, CFI = 0.96, GFI = 0.95, AGFI = 0.89, TLI = 0.93, RMSEA = 0.08). The reliability was confirmed with an alpha coefficient of 0.81 and an Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) of 0.98.
Conclusion: The Persian version of the OAB-V8 questionnaire demonstrated good validity and reliability, indicating its suitability for use in Persian-speaking countries.
Keywords: Overactive bladder scale; Persian; Psychometric properties; reliability and validity.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Translation and cross-cultural adaptation of Persian version of Evidence Based Medicine Questionnaire (EBMQ) in postgraduate medical students in Iran.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 16;19(4):e0301831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301831. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38626040 Free PMC article.
-
Validity and reliability of the TechPH scale in assessing Iranian older adults' attitudes toward technology.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Nov 5;24(1):907. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05502-3. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 39501176 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Malay Version Questionnaire to Evaluate Remote Health Monitoring of COVID-19 via Telehealth Applications: Navigating Telehealth Evolution.Cureus. 2024 Aug 23;16(8):e67579. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67579. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39310655 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of reliability and validity regarding the Chinese version of Critical Cultural Competence Scale for clinical nurses.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Oct 28;47(10):1425-1434. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210695. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36411694 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese, English.
-
Development and validation of a Decision-Making Ability Scale for postpartum urinary incontinence women engaging in pelvic floor physical therapy.Neurourol Urodyn. 2023 Nov;42(8):1756-1768. doi: 10.1002/nau.25282. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Neurourol Urodyn. 2023. PMID: 37723922 Review.
References
-
- Keshvari M., Nazari L., Yarmohmmadi A., Armin M. Evaluation of urodynamic changes, after the use of botulinum-a toxin injections into the detrusor, in patients with HTLV1 related detrusor over activity who are resistant to anticholinergic therapy. Medical Journal of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences. 2014;57(2):473–479. doi: 10.22038/mjms.2014.2683. - DOI
-
- Chapple C., Kelleher C., Siddiqui E., Andrae D.A., Johnson N., Payne C., et al. Validation of the overactive bladder-bladder assessment tool (OAB-BAT): a potential alternative to the standard bladder diary for monitoring OAB outcomes. European Urology Focus. 2021;7(5):1176–1183. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2020.12.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mahdavi R., Sheikhi Z., Golshan A. Effect of Botulinum neurotoxin type A injection in refractory idiopathic overactive bladder. North Khorasan University of Medical Sciences. 2011;3(2):75–80. doi: 10.29252/jnkums.3.2.75. - DOI
-
- Samadzadeh B., Najafloee R., Omrani H., Rezaei M. Efficacy of diltiazem plus tolterodine in treatment of overactive bladder after prostatectomy. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences. 2015;25(131):128–135. URL: http://jmums.mazums.ac.ir/files/site1/user_files_0d0bf0/nouri70-A-10-502....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous