AI-MARRVEL - A Knowledge-Driven AI System for Diagnosing Mendelian Disorders
- PMID: 38962029
- PMCID: PMC11221788
- DOI: 10.1056/aioa2300009
AI-MARRVEL - A Knowledge-Driven AI System for Diagnosing Mendelian Disorders
Abstract
Background: Diagnosing genetic disorders requires extensive manual curation and interpretation of candidate variants, a labor-intensive task even for trained geneticists. Although artificial intelligence (AI) shows promise in aiding these diagnoses, existing AI tools have only achieved moderate success for primary diagnosis.
Methods: AI-MARRVEL (AIM) uses a random-forest machine-learning classifier trained on over 3.5 million variants from thousands of diagnosed cases. AIM additionally incorporates expert-engineered features into training to recapitulate the intricate decision-making processes in molecular diagnosis. The online version of AIM is available at https://ai.marrvel.org. To evaluate AIM, we benchmarked it with diagnosed patients from three independent cohorts.
Results: AIM improved the rate of accurate genetic diagnosis, doubling the number of solved cases as compared with benchmarked methods, across three distinct real-world cohorts. To better identify diagnosable cases from the unsolved pools accumulated over time, we designed a confidence metric on which AIM achieved a precision rate of 98% and identified 57% of diagnosable cases out of a collection of 871 cases. Furthermore, AIM's performance improved after being fine-tuned for targeted settings including recessive disorders and trio analysis. Finally, AIM demonstrated potential for novel disease gene discovery by correctly predicting two newly reported disease genes from the Undiagnosed Diseases Network.
Conclusions: AIM achieved superior accuracy compared with existing methods for genetic diagnosis. We anticipate that this tool may aid in primary diagnosis, reanalysis of unsolved cases, and the discovery of novel disease genes. (Funded by the NIH Common Fund and others.).
Figures

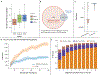
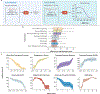

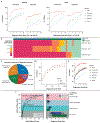
References
Grants and funding
- U01 HG007708/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007674/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007943/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG011795/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007942/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103555/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007709/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG010218/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS093793/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007530/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HG011311/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007703/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
