PD-L1 expression in keratinocyte and infiltration of CD4 + T lymphocyte can predict a severe type of erythema multiforme major induced by the anti-PD-1 antibody, pembrolizumab
- PMID: 38962048
- PMCID: PMC11217243
- DOI: 10.1007/s13691-024-00676-4
PD-L1 expression in keratinocyte and infiltration of CD4 + T lymphocyte can predict a severe type of erythema multiforme major induced by the anti-PD-1 antibody, pembrolizumab
Abstract
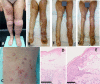
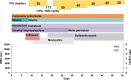
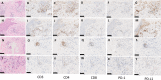
Skin toxicity is the most common adverse event of treatment with immune check point inhibitors. Among them, erythema multiforme is a rare occurrence with a frequency of 4%, with most of the cases developing grade 1/2 disease. We experienced high grade erythema multiforme major developing with pembrolizumab treatment for anal canal cancer with extensive skin metastases. Steroid ointment was ineffective, and the skin lesions with blisters expanded to > 45% of the body surface area. The patient was at risk for symptom aggravation, and a pulse therapy with methylprednisolone and increasing the dose of oral prednisolone (1 mg/kg) were started. The skin lesions improved in 1.8 months. Unless urgent and appropriate treatments such as high dose steroid administration were conducted, the skin toxicities could not be controlled. The presence of CD4+ T cells and PD-L1+ keratinocytes in the skin biopsy might be a predictive marker of erythema multiforme major resistant to standard steroid treatment.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13691-024-00676-4.
Keywords: Anti-PD-1 antibody; CD8+ T cell; Erythema multiforme major; PD-L1 expression; Severe cutaneous adverse reaction.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vesicular Contact Reaction May Progress into Erythema Multiforme.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2016 Dec;24(4):307-309. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2016. PMID: 28128086 Review.
-
Proliferative CD8(+) PD-1(+) T-cell infiltration in a pembrolizumab-induced cutaneous adverse reaction.Invest New Drugs. 2018 Dec;36(6):1138-1142. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0628-3. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Invest New Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29947012
-
Erythema multiforme as a rare skin manifestation during pembrolizumab treatment: a case report and literature review.J Chemother. 2025 Jun 2:1-5. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2025.2512264. Online ahead of print. J Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40454868
-
Steroid-refractory dermatologic and pulmonary toxicity in a patient on rituximab treated with pembrolizumab for progressive urothelial carcinoma: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2021 Mar 19;15(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02670-3. J Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33736690 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse cutaneous toxicities by PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors: pathogenesis, treatment, and surveillance.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2022 Mar;41(1):73-90. doi: 10.1080/15569527.2022.2034842. Epub 2022 Feb 20. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35107396 Review.
Cited by
-
PD-L1-CD80 interactions are required for intracellular signaling necessary for dendritic cell migration.Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 31;11(5):eadt3044. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adt3044. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 39879305 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
