Evaluation of the Effect of Benzydamine Hydrochloride on the Intensity of Gag Reflex: A Randomized Single-Blind Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38962077
- PMCID: PMC11217069
- DOI: 10.30476/dentjods.2023.97675.2032
Evaluation of the Effect of Benzydamine Hydrochloride on the Intensity of Gag Reflex: A Randomized Single-Blind Clinical Trial
Abstract
Statement of the problem: Gag reflex is among the most common problems during dental and endoscopic procedures. Benzydamine hydrochloride is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication and a local anesthetic that might be useful in reducing the gag reflex.
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the effects of benzydamine hydrochloride mouthwash on the intensity of the gag reflex.
Materials and method: In this randomized clinical trial study, 30 participants aged 21-26 with a gag trigger point index (GTPI) higher than 2 were divided into 2 groups. In the case group, 15 ml of 0.15% benzydamine hydrochloride mouthwash was gargled for 1 minute, and after 10 minutes GTPI test was conducted. In the control group, 4 puffs of 10% lidocaine spray were applied to the mucosa of the targeted area, and after 5 minutes, GTPI was measured. Participants were asked about the taste and smell of the medications.
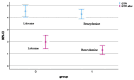
Results: GTPI was significantly reduced in both groups. In the lidocaine group, the GTPI score changed from 4.47 to 2.00 (p< 0.001), and that for the benzydamine group was 4.20 to 1.47 (p< 0.001). The variance rate of the gag reflex was -2.73 and -2.47 in the benzydamine group and lidocaine group, respectively. However, this reduction was not statistically significant between the two groups. Moreover, benzydamine mouthwash has a significantly better taste and smell than lidocaine (p= 0.001).
Conclusion: The results of this study showed that benzydamine mouthwash could be used quite effectively in reducing the gag reflex.
Keywords: Benzydamine; Gagging; Lidocaine; Local anesthetic; Reflex.
Copyright: © Journal of Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectivity of benzydamine hydrochloride gargle to reduce propofol consumption in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography procedure: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2020 May 23;20(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-00996-x. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32446304 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Altering the gag reflex via a palm pressure point.J Am Dent Assoc. 2008 Oct;139(10):1365-72. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2008.0048. J Am Dent Assoc. 2008. PMID: 18832272
-
Comparative study between benzydamine hydrochloride gel, lidocaine 5% gel and lidocaine 10% spray on endotracheal tube cuff as regards postoperative sore throat.Braz J Anesthesiol. 2016 May-Jun;66(3):242-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bjane.2014.09.007. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2016. PMID: 27108819
-
Topical benzydamine hydrochloride for prevention of postoperative sore throat in adults undergoing tracheal intubation for elective surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Anaesthesia. 2018 Jul;73(7):889-900. doi: 10.1111/anae.14224. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Anaesthesia. 2018. PMID: 29377080
-
Benzydamine hydrochloride on postoperative sore throat: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Can J Anaesth. 2014 Mar;61(3):220-8. doi: 10.1007/s12630-013-0080-y. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Can J Anaesth. 2014. PMID: 24263969 Review.
References
-
- Mosannen Mozafari P, Aboutorabzadeh SM, Azizi H, Khorasanchi M, Lotfinia Z, Motaghi S. Is laser acupuncture effective in controlling gag reflex while taking dental impressions? A randomized double-blinded sham-controlled clinical trial. J Evidence-Based Dental Practice. 2022; 22: 101733. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials