Cutting-edge developments in zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and applications for enhanced antimicrobial and UV protection in healthcare solutions
- PMID: 38962092
- PMCID: PMC11220610
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra02452d
Cutting-edge developments in zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and applications for enhanced antimicrobial and UV protection in healthcare solutions
Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive review of recent advancements in utilizing zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) to enhance antimicrobial and UV protective properties in healthcare solutions. It delves into the synthesis techniques of ZnO NPs and elucidates their antimicrobial efficacy, exploring the underlying mechanisms governing their action against a spectrum of pathogens. Factors impacting the antimicrobial performance of ZnO NPs, including size, surface characteristics, and environmental variables, are extensively analyzed. Moreover, recent studies showcasing the effectiveness of ZnO NPs against diverse pathogens are critically examined, underscoring their potential utility in combatting microbial infections. The study further investigates the UV protective capabilities of ZnO NPs, elucidating the mechanisms by which they offer UV protection and reviewing recent innovations in leveraging them for UV-blocking applications in healthcare. It also dissects the factors influencing the UV shielding performance of ZnO NPs, such as particle size, dispersion quality, and surface coatings. Additionally, the paper addresses challenges associated with integrating ZnO NPs into healthcare products and presents future perspectives for overcoming these hurdles. It emphasizes the imperative for continued research efforts and collaborative initiatives to fully harness the potential of ZnO NPs in developing advanced healthcare solutions with augmented antimicrobial and UV protective attributes. By advancing our understanding and leveraging innovative approaches, ZnO NPs hold promise for addressing pressing healthcare needs and enhancing patient care outcomes.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
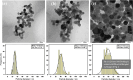

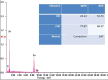
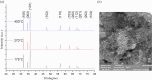

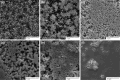



Similar articles
-
In-Vitro cytotoxicity, antibacterial, and UV protection properties of the biosynthesized Zinc oxide nanoparticles for medical textile applications.Microb Pathog. 2018 Dec;125:252-261. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.09.030. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30240818
-
Microbial synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential application as an antimicrobial agent and a feed supplement in animal industry: a review.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2019 Jul 9;10:57. doi: 10.1186/s40104-019-0368-z. eCollection 2019. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31321032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Modern Science and Technology: Multifunctional Roles in Healthcare, Environmental Remediation, and Industry.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 May 17;15(10):754. doi: 10.3390/nano15100754. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40423144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc oxide nanomaterials: Safeguarding food quality and sustainability.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2024 Nov;23(6):e70051. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70051. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2024. PMID: 39530622 Review.
-
Fabrication of Ultra-Pure Anisotropic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Simple and Cost-Effective Route: Implications for UTI and EAC Medications.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Jul;196(1):297-317. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01894-1. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 31529241
Cited by
-
Advancements in tantalum based nanoparticles for integrated imaging and photothermal therapy in cancer management.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 23;14(46):33681-33740. doi: 10.1039/d4ra05732e. eCollection 2024 Oct 23. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39450067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenic Zinc nanoparticles: green approach to synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial applications.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Jul 18;24(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02788-9. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40676579 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of strontium-based nanoparticles in modulating bone regeneration and antimicrobial resistance: a public health perspective.RSC Adv. 2025 Apr 7;15(14):10902-10957. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00308c. eCollection 2025 Apr 4. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40196828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green biosynthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles incorporated gellan gum hydrogel for biomedical application as wound dressing.Front Chem. 2025 Apr 17;13:1560213. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1560213. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40313399 Free PMC article.
-
Antrodia cinnamomea Residual Biomass-Based Hydrogel as a Novel UV-Protective and Antimicrobial Wound-Healing Dressing for Biomedical Use.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 8;26(10):4496. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104496. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osazee F. O. Mokobia K. E. Ifijen I. H. The Urgent Need for Tungsten-Based Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Agents. Biomed. Mater. Devices. 2023 doi: 10.1007/s44174-023-00127-3. - DOI
-
- Ifijen I. H., Maliki M., Udokpoh N. U. and Odiachi I. J., A Concise Review of the Antibacterial Action of Gold Nanoparticles Against Various Bacteria, in TMS 2023 152nd Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series, Springer, Cham, 2023, 10.1007/978-3-031-22524-6_58 - DOI
-
- Maliki M., Omorogbe S. O., Ifijen I. H., Aghedo O. N. and Ighodaro A., Incisive Review on Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Use in the Treatment of Bacterial Infections, in TMS 2023 152nd Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series, Springer, Cham, 2023, 10.1007/978-3-031-22524-6_44 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

