Fermented Aronia melanocarpa pomace improves the nutritive value of eggs, enhances ovarian function, and reshapes microbiota abundance in aged laying hens
- PMID: 38962144
- PMCID: PMC11220260
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1422172
Fermented Aronia melanocarpa pomace improves the nutritive value of eggs, enhances ovarian function, and reshapes microbiota abundance in aged laying hens
Abstract
Introduction: There is a decline in the quality and nutritive value of eggs in aged laying hens. Fruit pomaces with high nutritional and functional values have gained interest in poultry production to improve the performance.
Methods: The performance, egg nutritive value, lipid metabolism, ovarian health, and cecal microbiota abundance were evaluated in aged laying hens (320 laying hens, 345-day-old) fed on a basal diet (control), and a basal diet inclusion of 0.25%, 0.5%, or 1.0% fermented Aronia melanocarpa pomace (FAMP) for eight weeks.
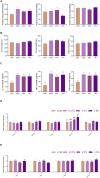
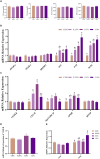
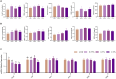
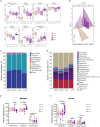
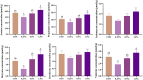
Results: The results show that 0.5% FAMP reduced the saturated fatty acids (such as C16:0) and improved the healthy lipid indices in egg yolks by decreasing the atherogenicity index, thrombogenic index, and hypocholesterolemia/hypercholesterolemia ratio and increasing health promotion index and desirable fatty acids (P < 0.05). Additionally, FAMP supplementation (0.25%-1.0%) increased (P < 0.05) the ovarian follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, and estrogen 2 levels, while 1.0% FAMP upregulated the HSD3B1 expression. The expression of VTG II and ApoVLDL II in the 0.25% and 0.5% FAMP groups, APOB in the 0.5% FAMP group, and ESR2 in the 1% FAMP group were upregulated (P < 0.05) in the liver. The ovarian total antioxidant capacity was increased (P < 0.05) by supplementation with 0.25%-1.0% FAMP. Dietary 0.5% and 1.0% FAMP downregulated (P < 0.05) the Keap1 expression, while 1.0% FAMP upregulated (P < 0.05) the Nrf2 expression in the ovary. Furthermore, 1.0% FAMP increased cecal acetate, butyrate, and valerate concentrations and Firmicutes while decreasing Proteobacteria (P < 0.05).
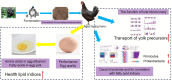
Conclusion: Overall, FAMP improved the nutritive value of eggs in aged laying hens by improving the liver-blood-ovary function and cecal microbial and metabolite composition, which might help to enhance economic benefits.
Keywords: aged laying hens; fermented Aronia melanocarpa pomace; microbiota; nutritive value; ovarian function.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Qin, Chen, Kong, Zhu, Azad, Cui, Lan and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aronia melanocarpa pomace enhances egg production and quality in late-laying hens via modulating gut microbiota and lipid metabolism.Br Poult Sci. 2025 Jul 28:1-15. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2025.2526157. Online ahead of print. Br Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40719240 Review.
-
Alpiniae oxyphyllae fructus improves production performance and egg quality of laying breeder hens by regulating reproductive hormones, antioxidant function, immunity and intestinal health.Poult Sci. 2024 Jun;103(6):103770. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103770. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38652955 Free PMC article.
-
Peppermint extract improves egg production and quality, increases antioxidant capacity, and alters cecal microbiota in late-phase laying hens.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 21;14:1252785. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1252785. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37808324 Free PMC article.
-
Feed Supplemented with Aronia melanocarpa (AM) Relieves the Oxidative Stress Caused by Ovulation in Peak Laying Hens and Increases the Content of Yolk Precursors.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 17;12(24):3574. doi: 10.3390/ani12243574. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552494 Free PMC article.
-
Ovary metabolome and cecal microbiota changes in aged laying hens supplemented with vitamin E.Poult Sci. 2024 Jun;103(6):103760. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103760. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38678750 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dietary Fermented Blueberry Pomace Supplementation Improves Small Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulates Cecal Microbiota in Aged Laying Hens.Animals (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;14(19):2786. doi: 10.3390/ani14192786. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409735 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary supplementation with Chinese herbal mixture extracts enhances growth performance, immunity, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal microbiota function in calves.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 8;12:1530124. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1530124. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40271489 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

