The comparison of DBS and RNS for adult drug-resistant epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38962148
- PMCID: PMC11220164
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1429223
The comparison of DBS and RNS for adult drug-resistant epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Neuromodulation has been proven to be a promising alternative treatment for adult patients with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE). Deep brain stimulation (DBS) and responsive neurostimulation (RNS) were approved by many countries for the treatment of DRE. However, there is a lack of systematic studies illustrating the differences between them. This meta-analysis is performed to assess the efficacy and clinical characteristics of DBS and RNS in adult patients with DRE.
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase were retrieved to obtain related studies including adult DRE patients who accepted DBS or RNS. The clinical characteristics of these patients were compiled for the following statistical analysis.
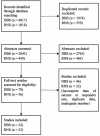
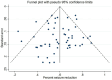
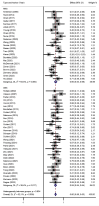
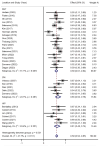
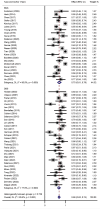
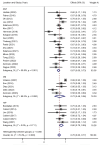
Results: A total of 55 studies (32 of DBS and 23 of RNS) involving 1,568 adult patients with DRE were included in this meta-analysis. There was no significant difference in seizure reduction and responder rate between DBS and RNS for DRE. The seizure reduction of DBS and RNS were 56% (95% CI 50-62%, p > 0.05) and 61% (95% CI 54-68%, p > 0.05). The responder rate of DBS and RNS were 67% (95% CI 58-76%, p > 0.05) and 71% (95% CI 64-78%, p > 0.05). Different targets of DBS did not show significant effect on seizure reduction (p > 0.05). Patients with DRE who accepted DBS were younger than those of RNS (32.9 years old vs. 37.8 years old, p < 0.01). The mean follow-up time was 47.3 months for DBS and 39.5 months for RNS (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Both DBS and RNS are beneficial and alternative therapies for adult DRE patients who are not eligible to accept resection surgery. Further and larger studies are needed to clarify the characteristics of different targets and provide tailored treatment for patients with DRE.
Keywords: deep brain stimulation; epilepsy; meta analysis; neuromodulation; responsive neurostimulation.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Shan, Wei and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alcala-Zermeno J. L., Gregg N. M., Wirrell E. C., Stead M., Worrell G. A., Van Gompel J. J., et al. (2021). Centromedian thalamic nucleus with or without anterior thalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for epilepsy in children and adults: a retrospective case series. Seizure 84, 101–107. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2020.11.012, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

