Activation of non-classical Wnt signaling pathway effectively enhances HLA-A presentation in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 38962268
- PMCID: PMC11219938
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1336106
Activation of non-classical Wnt signaling pathway effectively enhances HLA-A presentation in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Objective: The escape from T cell-mediated immune surveillance is an important cause of death for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). This study aims to identify clonal heterogeneity in leukemia progenitor cells and explore molecular or signaling pathways associated with AML immune escape.
Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed to identified AML-related cellular subsets, and intercellular communication was analyzed to investigate molecular mechanisms associated with AML immune escape. Bulk RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was performed to screen differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to hematopoietic stem cell progenitors (HSC-Prog) in AML, and critical ore signaling pathways and hub genes were found by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA), Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis. The mRNA level of the hub gene was verified using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and the protein level of human leukocyte antigen A (HLA-A) using enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA).
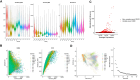
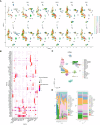
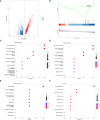
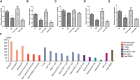
Results: scRNA-seq analysis revealed a large heterogeneity of HSC-Prog across samples, and the intercellular communication analysis indicated a strong association between HSC-Prog and CD8+-T cells, and HSC-Prog also had an association with HLA-A. Transcriptome analysis identified 1748 DEGs, enrichment analysis results showed that non-classical wnt signaling pathway was associated with AML, and 4 pathway-related genes (RHOA, RYK, CSNK1D, NLK) were obtained. After qRT-PCR and ELISA validation, hub genes and HLA-A were found to be down-regulated in AML and up-regulated after activation of the non-classical Wnt signaling pathway.
Conclusion: In this study, clonal heterogeneity of HSC-Prog cells in AML was identified, non-classical wnt signaling pathways associated with AML were identified, and it was verified that HLA-A could be upregulated by activation of non-classical wnt signaling, thereby increasing antigen presentation.
Keywords: HLA-A; acute myeloid leukemia; immune escape; non-classical Wnt signaling pathway; scRNA-seq.
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Yue, Gao, Zhou, Chen, Su, Yao, Shi, Zhao and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-363-3p promote the development of acute myeloid leukemia with RUNX1 mutation by targeting SPRYD4 and FNDC3B.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 May 7;100(18):e25807. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025807. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33950983 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomic profiling reveals immune cell heterogeneity in acute myeloid leukaemia peripheral blood mononuclear cells after chemotherapy.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Feb;47(1):97-112. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00853-2. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 37615858 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell data revealed the function of natural killer cells and macrophage cells in chemotherapy tolerance in acute myeloid leukemia.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 21;12:e18521. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18521. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39583114 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ferroptosis-related gene HSPB1 on acute myeloid leukemia.Int J Lab Hematol. 2024 Oct;46(5):899-909. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.14319. Epub 2024 Jun 2. Int J Lab Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38826023
-
Unveiling novel insights in acute myeloid leukemia through single-cell RNA sequencing.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 22;14:1365330. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1365330. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38711849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

