Preoperative sequential chemotherapy and hypofractionated radiotherapy combined with comprehensive surgical resection for high-risk soft tissue sarcomas: a retrospective study
- PMID: 38962275
- PMCID: PMC11219937
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1423151
Preoperative sequential chemotherapy and hypofractionated radiotherapy combined with comprehensive surgical resection for high-risk soft tissue sarcomas: a retrospective study
Abstract
Introduction: The management of soft tissue sarcomas presents considerable therapeutic challenges. This study was designed to assess the efficacy of neoadjuvant sequential chemotherapy and hypofractionated radiotherapy in conjunction with extensive surgical resection for the treatment of high-risk soft tissue sarcomas.
Materials and methods: We performed a retrospective review of 31 high-risk soft tissue sarcoma patients treated at our institution from June 2021 to June 2023. The cohort consisted of 21 males and 10 females with a mean age of 55.7 years and included both initial and recurrent disease presentations. Our treatment regimen comprised two to three cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy coupled with hypofractionated radiotherapy, delivered at 5 Gy per fraction to a total dose of 25-35 Gy across 5-7 days, prior to surgical resection aimed at achieving wide margins. Data collection was systematic, covering surgical outcomes, chemoradiotherapy-related complications, and prognostic factors.
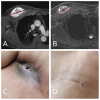
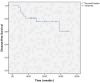
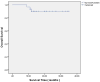
Results: All patients completed the prescribed course of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. 29% patients experienced grade 3+ chemotherapy toxicity, necessitating a reduction or interruption in their chemotherapy regimen. Limb preservation was accomplished in 30 patients finally. Response evaluation using RECIST 1.1 criteria post-neoadjuvant therapy revealed 9.7% with PD, 58.1% with SD, 29% with a PR, and 3.2% with a CR, culminating in an ORR of 32.2%. Postoperative complications included superficial wound infections in four patients and deep incisional infections in another four. 6 patients had developed metastasis, and 3 patients were still alive. Two experienced local recurrence. One-year DFS was 79.3%, with a one-year OS rate of 89.6%.
Conclusion: Neoadjuvant sequential chemotherapy and hypofractionated radiotherapy followed by extensive surgical resection represents an effective treatment paradigm for high-risk soft tissue sarcomas. This multimodal approach not only facilitates tumor reduction but also significantly reduces the risks of local recurrence and distant metastasis.
Keywords: high-risk soft; hypofractionated radiotherapy; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; sequential chemoradiotherapy; soft tissue sarcoma.
Copyright © 2024 Qu, Tian, Wang, Yang, Niu and Yao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neoadjuvant sequential chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for treatment of high-risk extremity soft tissue sarcoma: a single-institution experience.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2017;21(1):60-65. doi: 10.5114/wo.2017.66658. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2017. PMID: 28435400 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant hypofractionated radiotherapy and chemotherapy for extremity soft tissue sarcomas: Safety, feasibility, and early oncologic outcomes of a phase 2 trial.Radiother Oncol. 2021 Jun;159:161-167. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2021.03.033. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Radiother Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33798613 Clinical Trial.
-
Neoadjuvant Hypofractionated Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy in High-Grade Extremity Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Phase 2 Clinical Trial Protocol.JMIR Res Protoc. 2017 May 25;6(5):e97. doi: 10.2196/resprot.6806. JMIR Res Protoc. 2017. PMID: 28546135 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy for soft tissue sarcomas: JCOG Bone and Soft Tissue Tumor Study Group.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021 Feb 8;51(2):180-184. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyaa231. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33313851 Review.
-
Sarcomas of the head and neck.Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2003 Apr;12(2):379-417. doi: 10.1016/s1055-3207(03)00005-x. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2003. PMID: 12916461 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Myxoid Liposarcoma.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024 Oct;25(10):1289-1296. doi: 10.1007/s11864-024-01262-9. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39302575 Review.
-
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;17(7):1170. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071170. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227673 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ramey SJ, Yechieli R, Zhao W, Kodiyan J, Asher D, Chinea FM, et al. . Limb-sparing surgery plus radiotherapy results in superior survival: an analysis of patients with high-grade, extremity soft-tissue sarcoma from the NCDB and SEER. Cancer Med. (2018) 7:4228–39. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1625 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gronchi A, Palmerini E, Quagliuolo V, Martin Broto J, Lopez Pousa A, Grignani G, et al. . Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in high-Risk soft tissue sarcomas: final results of a randomized trial from italian (ISG), spanish (GEIS), french (FSG), and polish (PSG) sarcoma groups. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:2178–86. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.03289 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

