An updated review of the pharmacological effects and potential mechanisms of hederagenin and its derivatives
- PMID: 38962311
- PMCID: PMC11220241
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1374264
An updated review of the pharmacological effects and potential mechanisms of hederagenin and its derivatives
Abstract
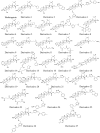
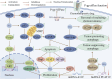
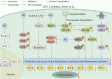
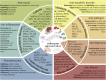
Hederagenin (HG) is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid that can be isolated from various medicinal herbs. By modifying the structure of HG, multiple derivatives with superior biological activities and safety profiles have been designed and synthesized. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that HG and its derivatives display multiple pharmacological activities against cancers, inflammatory diseases, infectious diseases, metabolic diseases, fibrotic diseases, cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, and depression. Previous studies have confirmed that HG and its derivatives combat cancer by exerting cytotoxicity, inhibiting proliferation, inducing apoptosis, modulating autophagy, and reversing chemotherapy resistance in cancer cells, and the action targets involved mainly include STAT3, Aurora B, KIF7, PI3K/AKT, NF-κB, Nrf2/ARE, Drp1, and P-gp. In addition, HG and its derivatives antagonize inflammation through inhibiting the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators by regulating inflammation-related pathways and targets, such as NF-κB, MAPK, JAK2/STAT3, Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1, and LncRNA A33/Axin2/β-catenin. Moreover, anti-pathogen, anti-metabolic disorder, anti-fibrosis, neuroprotection, and anti-depression mechanisms of HG and its derivatives have been partially elucidated. The diverse pharmacological properties of HG and its derivatives hold significant implications for future research and development of new drugs derived from HG, which can lead to improved effectiveness and safety profiles.
Keywords: anti-cancer; anti-inflammation; derivative; hederagenin; pharmacology.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hederagenin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via inhibiting long non-coding RNA A330074k22Rik/Axin2/β-catenin signalling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Nov;112:109247. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109247. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36155281
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of Khayandirobilide A from Khaya senegalensis via NF-κB, AP-1 and p38 MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 and BV-2 cells.Phytomedicine. 2018 Mar 15;42:152-163. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.03.016. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29655681
-
Ginseng-derived nanoparticles alleviate alcohol-induced liver injury by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway and inhibiting the NF-κB signalling pathway in vitro and in vivo.Phytomedicine. 2024 May;127:155428. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155428. Epub 2024 Feb 25. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38458086
-
A review of the biological activity and pharmacology of cryptotanshinone, an important active constituent in Danshen.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111332. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111332. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33548911 Review.
-
Advances in the anti-tumor potential of hederagenin and its analogs.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 15;959:176073. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176073. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37742813 Review.
Cited by
-
Hederagenin's uric acid-lowering effects in hyperuricemic mice: Mechanistic insights from molecular docking and in vivo analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 24;20(6):e0326317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326317. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40554493 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the Molecular Mechanisms of Hederagenin-Regulated Mitophagy in Cervical Cancer SiHa Cells through an Integrative Approach Combining Proteomics and Advanced Network Association Algorithm.J Proteome Res. 2025 Apr 4;24(4):2081-2095. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5c00022. Epub 2025 Mar 26. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 40135937 Free PMC article.
-
Hederagenin promotes SIRT6 to attenuate epidural scar formation by aggravating PRMT1 deacetylation.Bone Joint Res. 2025 Jun 13;14(6):516-526. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.146.BJR-2024-0287.R2. Bone Joint Res. 2025. PMID: 40511498 Free PMC article.
-
The Astragalus Membranaceus Herb Attenuates Leukemia by Inhibiting the FLI1 Oncogene and Enhancing Anti-Tumor Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 14;25(24):13426. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413426. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amaravadi R. K., Kimmelman A. C., Debnath J. (2019). Targeting autophagy in cancer: recent advances and future directions. Cancer Discov. 9 (9), 1167–1181. 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-19-0292 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

