Knowledge, attitudes and practices towards glycemic control among persons with diabetes mellitus at two tertiary hospitals in Uganda
- PMID: 38962346
- PMCID: PMC11217846
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v24i1.22
Knowledge, attitudes and practices towards glycemic control among persons with diabetes mellitus at two tertiary hospitals in Uganda
Abstract
Background: Intensive glycaemic control reduces the risk of microvascular complications in persons with diabetes mellitus (DM). Owing to limited data available, we aimed to determine the knowledge, attitude, and practices (KAPs) toward glycaemic control among Ugandans with DM at two large tertiary healthcare facilities.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among persons with DM attending outpatient clinics at Kiruddu National Referral Hospital (KNRH) and Mulago National Specialized Hospital (MNSH) between March and April 2022. Eligible participants provided written informed consent and were recruited through a systematic sampling technique and relevant data was collected using a pretested, interviewer-administered, semi-structured questionnaire.
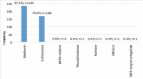
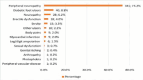
Results: Of the 452 participants, 318 (70.4%) were females. The median age was 52 years (IQR: 45-60 years), with more than two-thirds diagnosed with DM at ≥36 years (69.8%, n=310). Overall, 274 participants (60.6%) had good knowledge on glycemic control. At multivariable logistic regression analysis, good knowledge about glycaemic control was significantly associated with having received training on glycaemic control (aOR: 2.3, 95% CI: 1.4 - 3.7, p=0.002), level of education: diploma (aOR: 4.3, 95% CI: 1.1 - 17.8, p=0.042), degree aOR: 4.9, 95% CI: 1.0 - 23.1, p=0.046) compared to informal education, and nearest distance from the health facility (aOR: 3.1, 95% CI: 1.0 - 9.6, p=0.047).
Conclusions: More than half of the patients had good knowledge about glycaemic control and this was associated with level of education, distance from the health facility and having received training. Further studies assessing the correlations between actual level of glycaemic control and patient related KAPs are recommended.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; HbA1C; KAPs; glycemic control.
© 2024 Ninsiima D et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no completing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of glycemic control and related factors among outpatients with type 2 diabetes at Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Mar 7;22(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-00974-z. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35249547 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitude, practices and their associated factors towards diabetes mellitus among non diabetes community members of Bale Zone administrative towns, South East Ethiopia. A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 2;12(2):e0170040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170040. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28152066 Free PMC article.
-
Glycemic control and its associated factors among adult diabetic patients in Southern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.Afr Health Sci. 2024 Mar;24(1):187-197. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v24i1.23. Afr Health Sci. 2024. PMID: 38962352 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with glycaemic control and diabetes complications in patients at Bugando Medical Centre, Mwanza, Tanzania: A cross-sectional study design.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 30;19(8):e0308659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308659. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39213431 Free PMC article.
-
Poor glycemic control and its associated factors among children with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Harar, eastern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 Sep 28;23(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01453-9. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 37759193 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ADA, author. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(Supplement 1):S8–S16. doi:10.2337/DC15-S005. - PubMed
-
- WHO, author. Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. 2019;21 doi:10.5005/jp/books/12855_84.
-
- IDF, author. Diabetes Atlas. 2019;266 doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(55)92135-8.
-
- Bahendeka S, Wesonga R, Mutungi G, Muwonge J, Neema S, Guwatudde D. Prevalence and correlates of diabetes mellitus in Uganda: a population-based national survey. Trop Med Int Health. 2016;21(3):405–416. doi:10.1111/tmi.12663. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous