Single-cell transcriptome dissecting the microenvironment remodeled by PD1 blockade combined with photodynamic therapy in a mouse model of oral carcinogenesis
- PMID: 38962427
- PMCID: PMC11220179
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.636
Single-cell transcriptome dissecting the microenvironment remodeled by PD1 blockade combined with photodynamic therapy in a mouse model of oral carcinogenesis
Abstract
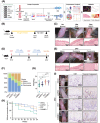
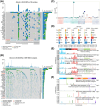
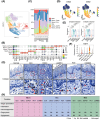
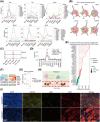
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) stands as a predominant and perilous malignant neoplasm globally, with the majority of cases originating from oral potential malignant disorders (OPMDs). Despite this, effective strategies to impede the progression of OPMDs to OSCC remain elusive. In this study, we established mouse models of oral carcinogenesis via 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide induction, mirroring the sequential transformation from normal oral mucosa to OPMDs, culminating in OSCC development. By intervening during the OPMDs stage, we observed that combining PD1 blockade with photodynamic therapy (PDT) significantly mitigated oral carcinogenesis progression. Single-cell transcriptomic sequencing unveiled microenvironmental dysregulation occurring predominantly from OPMDs to OSCC stages, fostering a tumor-promoting milieu characterized by increased Treg proportion, heightened S100A8 expression, and decreased Fib_Igfbp5 (a specific fibroblast subtype) proportion, among others. Notably, intervening with PD1 blockade and PDT during the OPMDs stage hindered the formation of the tumor-promoting microenvironment, resulting in decreased Treg proportion, reduced S100A8 expression, and increased Fib_Igfbp5 proportion. Moreover, combination therapy elicited a more robust treatment-associated immune response compared with monotherapy. In essence, our findings present a novel strategy for curtailing the progression of oral carcinogenesis.
Keywords: immune checkpoint blockade; multiomics; oral carcinogenesis; photodynamic therapy; single‐cell transcriptome sequencing.
© 2024 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors disclosed no relevant relationships.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigating Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in the Microenvironment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders (OPMDs): Can They Shift Our Perspective? A Scoping Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 18;14(2):606. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020606. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass cytometry and transcriptomic profiling reveal PD1 blockade induced alterations in oral carcinogenesis.Mol Carcinog. 2024 Apr;63(4):563-576. doi: 10.1002/mc.23670. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Mol Carcinog. 2024. PMID: 38085124
-
TNFα Signaling Is Increased in Progressing Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders and Regulates Malignant Transformation in an Oral Carcinogenesis Model.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 28;11:741013. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.741013. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34650923 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Proinflammatory, NF-kappaB Dependent Cytokines: IL-1α, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α in Tissue Specimens and Saliva of Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders.J Clin Med. 2020 Mar 21;9(3):867. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030867. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32245251 Free PMC article.
-
ICI-based therapies: A new strategy for oral potentially malignant disorders.Oral Oncol. 2023 May;140:106388. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2023.106388. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Oral Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37054586 Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(1):17‐48. - PubMed
-
- Harrington KJ, Ferris RL, Blumenschein G, et al. Nivolumab versus standard, single‐agent therapy of investigator's choice in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (CheckMate 141): health‐related quality‐of‐life results from a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(8):1104‐1115. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pinto AC, Caramês J, Francisco H, et al. Malignant transformation rate of oral leukoplakia—systematic review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2020;129(6):600‐611. e2. - PubMed
-
- Dong Y, Wang Z, Mao F, et al. PD‐1 blockade prevents the progression of oral carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2021;42(6):891‐902. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
