Neutrophil in the suppressed immune microenvironment: Critical prognostic factor for lung adenocarcinoma patients with KEAP1 mutation
- PMID: 38962454
- PMCID: PMC11220125
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1382421
Neutrophil in the suppressed immune microenvironment: Critical prognostic factor for lung adenocarcinoma patients with KEAP1 mutation
Abstract
Purpose: It is still unclear whether KEAP1 mutation is detrimental to immunotherapy of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patients, we try to analyse the exact changes in the TME in LUAD patients with KEAP1 mutations and to identify key factors influencing prognosis.
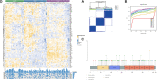
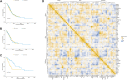
Experimental design: A total of 1,029 patients with lung squamous carcinoma (LUSC) or LUAD with data obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas were included in this study. The TME and OS of patients with LUAD stratified by mutant versus wild-type KEAP1 status were comprehensively measured. Moreover, we classified LUAD patients with KEAP1 mutations into three subtypes, by unsupervised consensus clustering. We further analysed the TME, OS, commutated genes and metabolic pathways of different subgroups. A total of 40 LUAD patients underwent immunotherapy were collected and classified into mutant KEAP1 group and wild-type KEAP1 group. We also conducted immunohistochemical staining in KEAP1-MT groups.
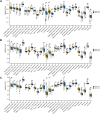
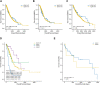
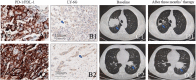
Result: Suppressed TME was observed not only in LUAD patients but also in LUSC patients. LUAD patients with mutant KEAP1 underwent immunotherapy had worse PFS than wild-type KEAP1. Unsupervised consensus clustering analysis suggested that the three subtypes of patients exhibited different densities of neutrophil infiltration and had different OS results: cluster 2 patients had significantly higher levels of neutrophils had significantly worse prognoses than those of patients in clusters 1 and 3 and patients with wild-type KEAP1. Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses proved that a high density of neutrophils was significantly associated with worse OS and immunohistochemical staining proved that shorter PFS showed high density of neutrophils.
Conclusion: KEAP1 mutation significantly suppresses the tumour immune microenvironment in LUAD patients. LUAD patients with mutant KEAP1 underwent immunotherapy had worse PFS than with wild-type KEAP1. Neutrophils may play an important role in the prognosis of LUAD patients with KEAP1 mutations and may provide a promising therapeutic target.
Keywords: KEAP1; NSCLC; lung adenocarcinoma; neutrophil; tumour microenvironment.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Wang, Liu, Ning, Chen and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
KEAP1-driven co-mutations in lung adenocarcinoma unresponsive to immunotherapy despite high tumor mutational burden.Ann Oncol. 2020 Dec;31(12):1746-1754. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.08.2105. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Ann Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32866624
-
Cancer Stemness-Based Prognostic Immune-Related Gene Signatures in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 21;12:755805. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.755805. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34745015 Free PMC article.
-
Diminished Efficacy of Programmed Death-(Ligand)1 Inhibition in STK11- and KEAP1-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma Is Affected by KRAS Mutation Status.J Thorac Oncol. 2022 Mar;17(3):399-410. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.10.013. Epub 2021 Nov 2. J Thorac Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34740862 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-Cancer Analysis of Immune Cell Infiltration Identifies a Prognostic Immune-Cell Characteristic Score (ICCS) in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 30;11:1218. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01218. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32714316 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of GLUT1 on the Survival Rate and Immune Cell Infiltration of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta and Bioinformatics Analysis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(2):223-238. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210708115406. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34238200 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

