The effectiveness and predictors influencing the outcome of onabotulinumtoxinA treatment in chronic migraine: understanding from diverse patient profiles in a single session
- PMID: 38962481
- PMCID: PMC11219632
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1417303
The effectiveness and predictors influencing the outcome of onabotulinumtoxinA treatment in chronic migraine: understanding from diverse patient profiles in a single session
Abstract
Objective: This real-world study aimed to investigate how onabotulinumtoxinA affects the outcome of migraine, along with accompanying anxiety, depression, and bruxism among a group of patients with chronic migraine (CM) and define predictors of good response.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with CM who received onabotulinumtoxinA were included in this single-center, real-world retrospective cohort study. Monthly headache days (MHDs), monthly migraine days (MMDs), headache intensity (numeric rating scale-NRS) and headache characteristics were evaluated at baseline and 12 weeks post-treatment. Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) included Migraine Disability Assessment Scale (MIDAS), Headache Impact Test-6 (HIT-6) scores, 12-item Allodynia Symptom Checklist (ASC-12), Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI). Response to onabotulinumtoxinA (% reduction in MHDs) and treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were also evaluated. OnabotulinumA was applied to the masseter muscles in patients complaining of bruxism.
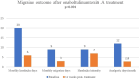
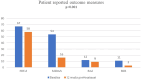
Results: A total of 72 patients (mean ± SD age: 36.3 ± 8.5 years; 91.7% were female) diagnosed with CM were included. OnabotulinumtoxinA revealed significant decrease in median (IQR) MHDs [from 20(15-25) at baseline to 6(4-10), p < 0.001], MMDs [from 9(6-12) to 3(1-6), p < 0.001] and NRS [from 9(8-10) to 7(6-8), p < 0.001], and the MIDAS [from 54(30-81) to 16(7-24), p < 0.001], HIT-6 [from 67(65-69) to 58(54-64), p < 0.001], ASC-12 [from 6(1.5-9) to 2(0-9), p = 0.002], BAI [from 12(6.5-19) to 9(3-17), p < 0.001] and BDI [from 11(6.5-17) to 3(2-7) p < 0.001] scores at 12 weeks post-treatment. Patients complaining of bruxism received onabotulinumtoxinA injections in the first n = 27 (37.5%) and 12. week post-treatment n = 19 (70.4%) periods. Overall, 70.8% of patients responded (≥50% reduction in MHDs), while 29.2% did not (<50% reduction). Both groups showed similar characteristics in demographics, migraine history, baseline PROMs scores, comorbidities, and prior treatments.
Conclusion: OnabotulinumtoxinA is an effective treatment option that rapidly improves migraine outcomes, disability, and impact while also alleviating comorbid depression and/or anxiety. This study's noteworthy finding is that onabotulinumtoxinA is effective in a majority of CM patients, irrespective of their prior treatment history, migraine characteristics, or concurrent comorbidities. Furthermore, we identified no specific predictors for a favorable response to onabotulinumtoxinA. Applying onabotulinumtoxinA to the masseter muscles can relieve discomfort associated with concurrent bruxism; however, it does not impact migraine outcomes.
Keywords: anxiety; bruxism; chronic migraine; depression; efficacy; onabotulinumtoxinA; outcome; predictors.
Copyright © 2024 Ilgaz Aydinlar, Erdogan Soyukibar and Yalinay Dikmen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of galcanezumab on sleep quality, migraine outcome, and multidimensional patient-reported outcome measures: a real-world experience in Turkish patients with episodic and chronic migraine.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 3;15:1411238. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1411238. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38887386 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and tolerability of atogepant in the prevention of migraine: A real life, prospective, multicentric study (the STAR study).Cephalalgia. 2025 Apr;45(4):3331024251335927. doi: 10.1177/03331024251335927. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Cephalalgia. 2025. PMID: 40267275
-
Long-term (48 weeks) effectiveness, safety, and tolerability of erenumab in the prevention of high-frequency episodic and chronic migraine in a real world: Results of the EARLY 2 study.Headache. 2021 Oct;61(9):1351-1363. doi: 10.1111/head.14194. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Headache. 2021. PMID: 34309862
-
Real-World Evidence for Control of Chronic Migraine Patients Receiving CGRP Monoclonal Antibody Therapy Added to OnabotulinumtoxinA: A Retrospective Chart Review.Pain Ther. 2021 Dec;10(2):809-826. doi: 10.1007/s40122-021-00264-x. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Pain Ther. 2021. PMID: 33880725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High efficacy of onabotulinumtoxinA treatment in patients with comorbid migraine and depression: a meta-analysis.J Transl Med. 2021 Mar 31;19(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02801-w. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33789668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

