Successful Management of Upper Gastrointestinal Obstruction With Primary Advanced Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 38962539
- PMCID: PMC11215435
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10347
Successful Management of Upper Gastrointestinal Obstruction With Primary Advanced Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
Background/aim: Upper gastrointestinal obstruction is an extremely rare complication of primary ovarian cancer. We present a case of primary advanced ovarian cancer with gastroduodenal obstruction successfully managed with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and conservative treatment.
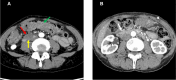
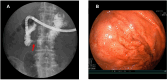
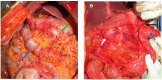
Case report: A 60-year-old woman was referred to our hospital for advanced ovarian cancer with upper gastrointestinal obstruction. Computed tomography and endoscopy revealed severe duodenal obstruction caused by dissemination. NAC was initiated with conservative management using a nasogastric tube and total parenteral nutrition (TPN). She was able to eat and TPN was stopped after three months. Complete resection was achieved with interval debulking surgery (IDS) not involving pancreatoduodenectomy, which would have been necessary for primary debulking surgery. There were no serious postoperative complications.
Conclusion: NAC with conservative management can improve upper gastrointestinal obstruction in patients with primary advanced ovarian cancer. Furthermore, IDS is expected to allow complete resection, avoiding highly invasive surgeries.
Keywords: Upper gastrointestinal tract; cytoreductive surgery; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; ovarian cancer; pancreaticoduodenectomy.
Copyright 2024, International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Krebs HB, Goplerud DR. Surgical management of bowel obstruction in advanced ovarian carcinoma. Obstet Gynecol. 1983;61:327–330. - PubMed
-
- Redman CW, Shafi MI, Ambrose S, Lawton FG, Blackledge GR, Luesley DM, Fielding JW, Chan KK. Survival following intestinal obstruction in ovarian cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1988;14:383–386. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
